Francisco Church is a rehabilitation specialist and the chief editor of Recovery Ranger. He creates this site to offer guidance and support to individuals seeking...Read more
Drug-induced lupus is a common, but potentially serious, form of lupus that can occur when certain prescription drugs are taken. If left untreated, drug-induced lupus can cause joint pain, fatigue, fever, and in some cases, organ damage. While there is no cure for drug-induced lupus, it is possible to successfully manage the condition with the right approach. In this article, we will look at the signs and symptoms of drug-induced lupus, discuss the available treatments, and provide some tips on how to treat this condition.
Treating Drug-Induced Lupus
- Visit your doctor to discuss your symptoms and medical history.
- Your doctor may suggest blood tests to identify antibodies associated with lupus.
- If drug-induced lupus is suspected, your doctor will likely suggest that you discontinue the medication.
- Your doctor may suggest additional medications to reduce inflammation and pain.
- Your doctor may suggest lifestyle changes, such as rest, a healthy diet, and exercise.
- Follow-up visits may be necessary to monitor your condition.
Contents
- Overview of Drug-Induced Lupus
- Diagnosis of Drug-Induced Lupus
- Treatment of Drug-Induced Lupus
- Alternative Therapies for Drug-Induced Lupus
- Frequently Asked Questions
- What is Drug Induced Lupus?
- What Medications Cause Drug Induced Lupus?
- How is Drug Induced Lupus Diagnosed?
- How is Drug Induced Lupus Treated?
- Are there Any Complications from Drug Induced Lupus?
- What is the Prognosis for Drug Induced Lupus?
- Is Diethylpropion A Stimulant?
- Is Alcohol A Inflammatory?
- Does Alcohol Make A Uti Worse?
Overview of Drug-Induced Lupus
Drug-induced lupus is a type of lupus caused by certain prescription medications. It is a form of autoimmune disease, which is when the body’s own immune system attacks and damages its own healthy cells and tissues. Symptoms of drug-induced lupus can include fatigue, joint pain, skin rash, fever, and anemia. Treatment involves discontinuing the drug that is causing the lupus and treating any symptoms that may arise with medications, lifestyle changes, and alternative therapies.
Diagnosis of Drug-Induced Lupus
In order to diagnose drug-induced lupus, a physician will typically conduct a physical exam, review medical history, and order laboratory tests. The doctor will also ask questions about any medications the patient is taking or has taken recently. Blood tests can be used to determine if there are any antibodies present that are associated with lupus. Imaging tests such as X-rays and MRIs can also be used to look for inflammation and damage to organs. If the doctor suspects drug-induced lupus, they may take a biopsy of the affected tissue or organs.
Signs and Symptoms
Signs and symptoms of drug-induced lupus are similar to those of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Common signs and symptoms include joint pain, fatigue, skin rash, fever, and anemia. Other symptoms may include chest pain, weight loss, hair loss, dry eyes, and cognitive problems.
Causes of Drug-Induced Lupus
Drug-induced lupus is caused by certain medications. These medications include some antibiotics, antidepressants, seizure medications, and heart medications. Other drugs that have been known to cause drug-induced lupus include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), anticonvulsants, and chemotherapy drugs.
Treatment of Drug-Induced Lupus
Treatment of drug-induced lupus typically involves discontinuing the medication that is causing the lupus. The doctor may also prescribe medications to reduce inflammation and pain, as well as medications to help with any other symptoms that may arise.
Medications
Medications used to treat drug-induced lupus include corticosteroids, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), antimalarial drugs, immunosuppressive drugs, and biologic drugs. Corticosteroids are used to reduce inflammation. NSAIDs are used to reduce pain and swelling. Antimalarial drugs are used to reduce inflammation and pain. Immunosuppressive drugs are used to suppress the immune system and reduce inflammation. Biologic drugs are used to stop the immune system from attacking healthy cells and tissues.
Lifestyle Changes
In addition to medications, lifestyle changes may be recommended to help manage drug-induced lupus. These changes may include getting enough rest, eating a balanced diet, avoiding triggering foods, exercising regularly, and managing stress. It is also important to avoid exposure to sunlight, as this can worsen lupus symptoms.
Alternative Therapies for Drug-Induced Lupus
Alternative therapies may be recommended to help manage the symptoms of drug-induced lupus. These therapies include massage, acupuncture, yoga, and relaxation techniques. Herbal supplements, such as curcumin, have also been found to be helpful in reducing inflammation and pain. Additionally, omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish oil, may help reduce inflammation and improve overall health.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Drug Induced Lupus?
Drug induced lupus is a type of lupus that is caused by taking certain medications. It is an autoimmune disorder, meaning it is caused when the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue. Symptoms usually start shortly after taking the medication and may include joint pain, fatigue, skin rashes, fever, and a variety of other symptoms.
What Medications Cause Drug Induced Lupus?
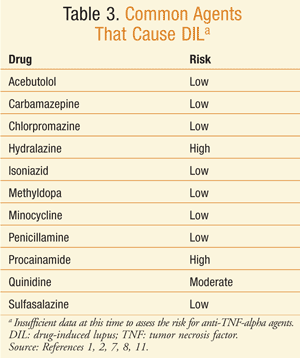
Drug induced lupus is most commonly caused by medications used to treat high blood pressure, heart conditions, and mental health issues. These medications include hydralazine, procainamide, isoniazid, quinidine, chlorpromazine, and other drugs.
How is Drug Induced Lupus Diagnosed?
Drug induced lupus is diagnosed through a physical exam, laboratory tests, and an analysis of the patient’s medical history. The doctor may also order imaging tests to check for inflammation or other signs of lupus.
How is Drug Induced Lupus Treated?
The first step in treating drug induced lupus is to stop taking the medication that is causing the issue. The doctor may also prescribe corticosteroids, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, or antimalarial medications to help reduce inflammation. In some cases, the doctor may also recommend physical therapy or lifestyle changes such as getting more exercise, eating a healthy diet, and reducing stress.
Are there Any Complications from Drug Induced Lupus?
Yes, there can be complications from drug induced lupus. These include an increased risk of infection, kidney failure, and other organ damage. In some cases, the lupus may also cause inflammation of the heart, lungs, or other organs.
What is the Prognosis for Drug Induced Lupus?
The prognosis for drug induced lupus is generally good, as long as the patient stops taking the medication that is causing the issue and follows the doctor’s treatment plan. In most cases, the symptoms will improve or even go away completely with treatment. However, some patients may have more severe symptoms that require ongoing treatment.
In conclusion, treating drug-induced lupus is a complex process that requires careful monitoring and management. It is important to seek advice from a healthcare professional and take any medications prescribed to reduce the symptoms and prevent complications. Patients should also learn as much as they can about the condition, its causes and possible treatments, and strive to lead a healthy lifestyle. With proper medication, lifestyle management and support, drug-induced lupus can be managed, allowing patients to enjoy a healthy and fulfilling life.
Francisco Church is a rehabilitation specialist and the chief editor of Recovery Ranger. He creates this site to offer guidance and support to individuals seeking to overcome addiction and achieve lasting sobriety. With extensive experience in the field of addiction treatment, Francisco is dedicated to helping individuals access the resources they need for successful recovery.
- Latest Posts by Francisco Church
-
Is Diethylpropion A Stimulant?
- -
Is Alcohol A Inflammatory?
- -
Does Alcohol Make A Uti Worse?
- All Posts