Francisco Church is a rehabilitation specialist and the chief editor of Recovery Ranger. He creates this site to offer guidance and support to individuals seeking...Read more
Drugs are powerful substances that can be used to treat a variety of conditions, but they can also have serious side effects. One of the most serious side effects of certain drugs is the formation of blood clots in the lungs, which can have life-threatening consequences. In this article, we will explore the link between drugs and blood clots in the lungs, including the causes and possible treatments. We’ll also look at how to identify and prevent this potentially dangerous side effect.
Yes, drugs can cause blood clots in the lungs. Some of the most common drugs that can cause blood clots in the lungs are oral contraceptives, cancer drugs, and anticoagulants. Other drugs, such as antiplatelet drugs, can also increase the risk of developing pulmonary embolism.
Contents
- Can Drugs Increase the Risk of Blood Clots in the Lungs?
- What Are the Symptoms of Blood Clots in the Lungs?
- Can Blood Clots in the Lungs Be Prevented?
- Few Frequently Asked Questions
- Can Drugs Cause Blood Clots in the Lungs?
- What Symptoms Indicate Blood Clots in the Lungs?
- What Treatment is Available for Blood Clots in the Lungs?
- Who is at Risk for Developing Blood Clots in the Lungs?
- What Complications Can Arise From Blood Clots in the Lungs?
- What Steps Can Be Taken to Reduce the Risk of Blood Clots in the Lungs?
- Pulmonary Embolism: Blood Clot in Lungs
- Is Diethylpropion A Stimulant?
- Is Alcohol A Inflammatory?
- Does Alcohol Make A Uti Worse?
Can Drugs Increase the Risk of Blood Clots in the Lungs?
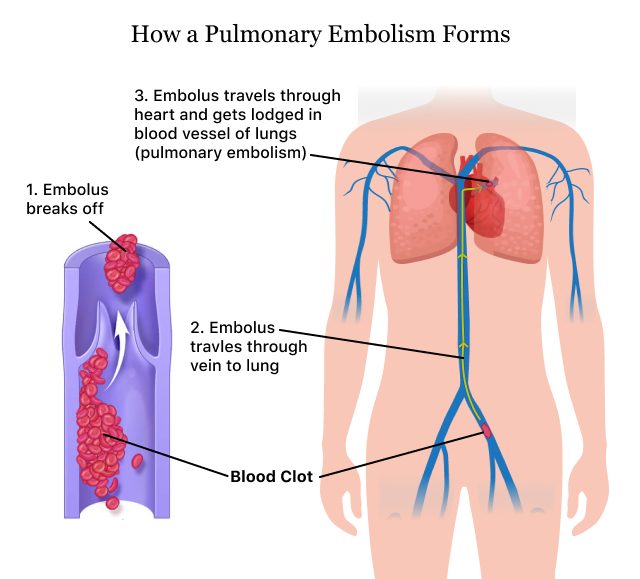
Blood clots in the lungs, also known as pulmonary embolism, can be very dangerous and may even be fatal. They are caused by the obstruction of a pulmonary artery by a clot, usually originating from a vein in the leg or arm. While there are many potential causes of these clots, one of them is the use of certain drugs.
The risk of blood clots in the lungs increases with certain drugs, including hormonal contraceptives, certain anticoagulants, and certain chemotherapy drugs. Hormonal contraceptives, such as birth control pills, contain estrogen and progestin, which can increase the risk of clotting. Anticoagulants, such as warfarin and heparin, are used to reduce the risk of clots, but can also increase the risk of pulmonary embolism when taken in high doses or when used for long periods of time. Finally, certain chemotherapy drugs, such as doxorubicin and cisplatin, can damage the walls of the veins and increase the risk of clot formation.
What Are the Symptoms of Blood Clots in the Lungs?
The symptoms of pulmonary embolism can vary depending on the size and location of the clot. Common symptoms include shortness of breath, chest pain, rapid heart rate, coughing, and feeling lightheaded or faint. In some cases, the symptoms may be subtle and can be mistaken for other conditions.
If you are taking any of the drugs mentioned above and experience any of the symptoms listed, it is important to seek medical attention immediately.
Diagnosis of Pulmonary Embolism
The diagnosis of pulmonary embolism is based on a combination of physical examination, imaging tests, and laboratory tests. These tests can help identify the presence of a clot and the underlying cause.
A physical examination may reveal signs of a clot, such as swelling and tenderness in the affected area. Imaging tests, such as an X-ray or CT scan, can be used to detect clots in the lungs. Finally, laboratory tests, such as a D-dimer test, can be used to detect the presence of clots in the bloodstream.
Treatment of Pulmonary Embolism
The treatment of pulmonary embolism depends on the size and location of the clot. Smaller clots may be treated with anticoagulants, such as warfarin or heparin, to prevent the clot from growing. Larger clots may require surgery to remove them. In some cases, clot-dissolving drugs may also be used.
In addition to medical treatment, lifestyle changes may be necessary to reduce the risk of further clot formation. These changes may include limiting the use of certain drugs, quitting smoking, and maintaining a healthy weight.
Can Blood Clots in the Lungs Be Prevented?
The best way to prevent blood clots in the lungs is to reduce the risk factors associated with them. This includes quitting smoking, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding certain drugs, such as hormonal contraceptives.
In addition, individuals who are at higher risk for clot formation may be prescribed anticoagulants, such as warfarin or heparin, to reduce their risk. It is important to talk to your doctor if you are concerned about your risk of pulmonary embolism.
Risks of Anticoagulants
Although anticoagulants can reduce the risk of pulmonary embolism, they also carry risks of their own. These risks include an increased risk of bleeding and the potential for drug interactions. It is important to talk to your doctor about the risks and benefits of taking anticoagulants before starting them.
Conclusion
Blood clots in the lungs can be a serious and potentially fatal condition. While there are many potential causes, the use of certain drugs can increase the risk of clot formation. It is important to talk to your doctor if you are concerned about your risk of pulmonary embolism and to follow their recommendations to reduce your risk.
Few Frequently Asked Questions
Can Drugs Cause Blood Clots in the Lungs?
Answer: Yes, certain drugs can cause blood clots in the lungs. Blood clots in the lungs, also known as pulmonary embolisms, occur when a clot in a vein or artery in the body breaks off and travels to the lungs, where it can block the flow of blood. This can potentially be fatal. Several medications, such as birth control pills, hormone replacement therapy drugs, and some cancer treatments, can increase the risk of developing blood clots in the lungs. It is important to discuss the risks of these medications with a doctor before taking them.
What Symptoms Indicate Blood Clots in the Lungs?
Answer: Symptoms of blood clots in the lungs can include shortness of breath, chest pain, coughing, coughing up blood, rapid heart rate, and sweating. If any of these symptoms occur, it is important to seek medical attention right away, as blood clots in the lungs can be life-threatening.
What Treatment is Available for Blood Clots in the Lungs?
Answer: Treatment for blood clots in the lungs usually involves a combination of medications and lifestyle changes. Medications such as anticoagulants, thrombolytics, and antiplatelet medications may be used to help dissolve the clot. In addition, lifestyle changes may be recommended to reduce the risk of clotting, such as quitting smoking, eating a healthy diet, and getting regular exercise.
Who is at Risk for Developing Blood Clots in the Lungs?
Answer: People who are at higher risk for developing blood clots in the lungs include those who are pregnant, have recently had surgery or have been immobile for a long period of time, have a family history of blood clots, have an underlying medical condition, or are taking certain medications. It is important to be aware of these risk factors and discuss them with a doctor.
What Complications Can Arise From Blood Clots in the Lungs?
Answer: Blood clots in the lungs can lead to several complications, including difficulty breathing, decreased oxygen levels in the blood, and damage to the heart and lungs. If the clot is not treated promptly, it can result in death.
What Steps Can Be Taken to Reduce the Risk of Blood Clots in the Lungs?
Answer: Several measures can be taken to reduce the risk of developing blood clots in the lungs. These include quitting smoking, exercising regularly, avoiding sitting for long periods of time, and eating a healthy diet. It is also important to talk to a doctor about any medications that may increase the risk of blood clots, and to follow any instructions for taking the medications.
Pulmonary Embolism: Blood Clot in Lungs
In conclusion, it is evident that drugs can cause blood clots in the lungs. These clots can be life-threatening and should be taken seriously. People who use drugs should be aware of the risks associated with them and seek medical attention if they experience any symptoms of pulmonary embolism. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential for a successful recovery.
Francisco Church is a rehabilitation specialist and the chief editor of Recovery Ranger. He creates this site to offer guidance and support to individuals seeking to overcome addiction and achieve lasting sobriety. With extensive experience in the field of addiction treatment, Francisco is dedicated to helping individuals access the resources they need for successful recovery.
- Latest Posts by Francisco Church
-
Is Diethylpropion A Stimulant?
- -
Is Alcohol A Inflammatory?
- -
Does Alcohol Make A Uti Worse?
- All Posts