Francisco Church is a rehabilitation specialist and the chief editor of Recovery Ranger. He creates this site to offer guidance and support to individuals seeking...Read more
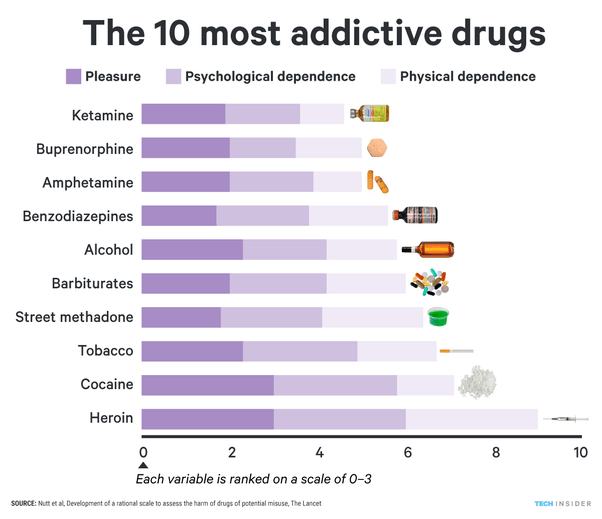
Drug addiction is a major issue in our world today and affects millions of individuals and their families. The most addictive drugs are those that have a high potential for abuse and are difficult to quit due to their powerful psychological and physical effects. In this article, we will explore what the most addictive drugs are and the consequences of their use. We will discuss the harmful effects they can have on the user and those around them and how they can be avoided. We will also provide resources to those with drug addiction and their families in order to find help.
Contents
- What is the Most Addictive Drug?
- Cocaine
- Heroin
- Methamphetamine
- Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the Most Addictive Drug?
- How Does Nicotine Affect the Body?
- What are the Effects of Nicotine Addiction?
- What are Some Signs of Nicotine Addiction?
- What are Some Treatment Options for Nicotine Addiction?
- Can Nicotine Addiction be Cured?
- Ask Dr. Nandi: The five most addictive substances in the world
- Is Diethylpropion A Stimulant?
- Is Alcohol A Inflammatory?
- Does Alcohol Make A Uti Worse?
What is the Most Addictive Drug?
Cocaine
Cocaine is one of the most addictive drugs on the market today. It is a stimulant drug that is derived from the coca plant, and can be snorted, smoked, or injected. Cocaine has been known to cause feelings of euphoria and intense pleasure, which can make it highly addictive for some users. The effects of cocaine can last for up to an hour, and it can be very difficult to stop using once someone has started. Cocaine is also one of the most expensive illicit drugs, which can make it even more desirable for users.
Cocaine addiction can lead to a number of physical and psychological health problems. It can cause serious cardiovascular issues, such as heart attack or stroke. It can also lead to serious mental health problems, such as depression or anxiety. Long-term cocaine use can also lead to organ damage, including damage to the brain, kidneys, and liver.
The withdrawal symptoms associated with cocaine addiction can be difficult to manage. Common withdrawal symptoms include intense cravings, depression, irritability, and fatigue. These symptoms can make it difficult for an individual to stop using cocaine, and can also make it difficult for them to maintain sobriety.
Physical Effects of Cocaine
The physical effects of cocaine can be quite severe. It can cause an increased heart rate and blood pressure, as well as increased sweating, insomnia, and restlessness. It can also cause the user to experience paranoia, hallucinations, and even seizures. These effects can be exacerbated if the user is taking other drugs in addition to cocaine.
Cocaine can also cause long-term physical damage. Chronic users may experience organ damage, such as damage to the heart, liver, and kidneys. It can also cause damage to the brain, leading to cognitive impairments, such as memory loss or difficulty with concentration.
Treatment for Cocaine Addiction
The treatment for cocaine addiction depends on the severity of the addiction. In some cases, detoxification is necessary in order to help the user manage their withdrawal symptoms. In other cases, cognitive-behavioral therapy may be necessary in order to help the user identify and change the behaviors that lead to cocaine use.
In addition to medical and psychological treatment, support groups can be beneficial for individuals struggling with cocaine addiction. Support groups provide a safe and supportive environment for users to discuss their experiences and issues related to their addiction. They can also provide a sense of community and accountability for individuals who are trying to stay sober.
Heroin
Heroin is one of the most addictive drugs on the market today. It is an opioid drug derived from the opium poppy, and is typically injected, snorted, or smoked. Heroin is known to produce intense feelings of euphoria, relaxation, and pleasure, which can make it highly addictive for some users. It can also be very difficult to stop using once someone has become addicted.
Heroin addiction can lead to a number of physical and psychological health problems. It can cause serious cardiovascular issues, such as heart attack or stroke. It can also lead to serious mental health problems, such as depression or anxiety. Long-term heroin use can also lead to organ damage, including damage to the brain, kidneys, and liver.
The withdrawal symptoms associated with heroin addiction can be very difficult to manage. Common withdrawal symptoms include intense cravings, restlessness, insomnia, and nausea. These symptoms can make it difficult for an individual to stop using heroin, and can also make it difficult for them to maintain sobriety.
Physical Effects of Heroin
The physical effects of heroin can be quite severe. It can cause an increased heart rate and blood pressure, as well as increased sweating, insomnia, and restlessness. It can also cause the user to experience paranoia, hallucinations, and even seizures. These effects can be exacerbated if the user is taking other drugs in addition to heroin.
Heroin can also cause long-term physical damage. Chronic users may experience organ damage, such as damage to the heart, liver, and kidneys. It can also cause damage to the brain, leading to cognitive impairments, such as memory loss or difficulty with concentration.
Treatment for Heroin Addiction
The treatment for heroin addiction depends on the severity of the addiction. In some cases, detoxification is necessary in order to help the user manage their withdrawal symptoms. In other cases, cognitive-behavioral therapy may be necessary in order to help the user identify and change the behaviors that lead to heroin use.
In addition to medical and psychological treatment, support groups can be beneficial for individuals struggling with heroin addiction. Support groups provide a safe and supportive environment for users to discuss their experiences and issues related to their addiction. They can also provide a sense of community and accountability for individuals who are trying to stay sober.
Methamphetamine
Methamphetamine is one of the most addictive drugs on the market today. It is a stimulant drug that is typically smoked, injected, or snorted. Methamphetamine is known to produce intense feelings of euphoria, energy, and focus, which can make it highly addictive for some users. It can also be very difficult to stop using once someone has become addicted.
Methamphetamine addiction can lead to a number of physical and psychological health problems. It can cause serious cardiovascular issues, such as heart attack or stroke. It can also lead to serious mental health problems, such as depression or anxiety. Long-term methamphetamine use can also lead to organ damage, including damage to the brain, kidneys, and liver.
The withdrawal symptoms associated with methamphetamine addiction can be difficult to manage. Common withdrawal symptoms include intense cravings, restlessness, insomnia, and fatigue. These symptoms can make it difficult for an individual to stop using methamphetamine, and can also make it difficult for them to maintain sobriety.
Physical Effects of Methamphetamine
The physical effects of methamphetamine can be quite severe. It can cause an increased heart rate and blood pressure, as well as increased sweating, insomnia, and restlessness. It can also cause the user to experience paranoia, hallucinations, and even seizures. These effects can be exacerbated if the user is taking other drugs in addition to methamphetamine.
Methamphetamine can also cause long-term physical damage. Chronic users may experience organ damage, such as damage to the heart, liver, and kidneys. It can also cause damage to the brain, leading to cognitive impairments, such as memory loss or difficulty with concentration.
Treatment for Methamphetamine Addiction
The treatment for methamphetamine addiction depends on the severity of the addiction. In some cases, detoxification is necessary in order to help the user manage their withdrawal symptoms. In other cases, cognitive-behavioral therapy may be necessary in order to help the user identify and change the behaviors that lead to methamphetamine use.
In addition to medical and psychological treatment, support groups can be beneficial for individuals struggling with methamphetamine addiction. Support groups provide a safe and supportive environment for users to discuss their experiences and issues related to their addiction. They can also provide a sense of community and accountability for individuals who are trying to stay sober.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Most Addictive Drug?
Answer: The most addictive drug is nicotine, which is found in cigarettes, cigars, and other forms of tobacco. Nicotine is highly addictive and can cause physical, psychological, and social problems. Nicotine addiction is one of the leading causes of preventable death in the United States.
How Does Nicotine Affect the Body?
Answer: Nicotine has numerous effects on the body, including an increase in heart rate and blood pressure, as well as an increase in dopamine production in the brain, leading to a feeling of pleasure and satisfaction. Over time, the body can become physically dependent on nicotine, making it difficult to quit.
What are the Effects of Nicotine Addiction?
Answer: Nicotine addiction can lead to numerous physical, psychological, and social consequences. Physically, nicotine addiction is linked to an increased risk of cancer, heart disease, and stroke. Psychologically, nicotine addiction can lead to increased stress, anxiety, and depression. Socially, nicotine addiction can lead to strained relationships, as well as difficulty in school or work.
What are Some Signs of Nicotine Addiction?
Answer: Some signs of nicotine addiction include a strong craving for nicotine, difficulty quitting, feeling irritable or anxious when unable to use nicotine, and using more than intended. Other signs include financial and legal problems related to nicotine use, as well as social and family issues.
What are Some Treatment Options for Nicotine Addiction?
Answer: Treatment options for nicotine addiction include medications, such as nicotine replacement therapy, as well as behavioral therapies, such as cognitive behavioral therapy, motivational interviewing, and contingency management. In addition, self-help groups, such as Nicotine Anonymous, can be beneficial for those looking to quit.
Can Nicotine Addiction be Cured?
Answer: While there is no cure for nicotine addiction, it is possible to quit and reduce the risks associated with nicotine use. Quitting smoking can lead to numerous health benefits, including improved cardiovascular health and a lower risk of certain cancers. It is important to seek treatment when trying to quit, as it can improve the chances of success.
Ask Dr. Nandi: The five most addictive substances in the world
In conclusion, it is clear that there is no single “most addictive drug”, as the addictive potential of any drug can vary greatly depending on a variety of factors. That being said, substances such as heroin, cocaine, methamphetamine and alcohol are amongst some of the most widely abused and potentially addictive drugs available. As such, it is important for individuals to be aware of the risks associated with these and other drugs, and to make informed decisions when it comes to their use.
Francisco Church is a rehabilitation specialist and the chief editor of Recovery Ranger. He creates this site to offer guidance and support to individuals seeking to overcome addiction and achieve lasting sobriety. With extensive experience in the field of addiction treatment, Francisco is dedicated to helping individuals access the resources they need for successful recovery.
- Latest Posts by Francisco Church
-
Is Diethylpropion A Stimulant?
- -
Is Alcohol A Inflammatory?
- -
Does Alcohol Make A Uti Worse?
- All Posts