Francisco Church is a rehabilitation specialist and the chief editor of Recovery Ranger. He creates this site to offer guidance and support to individuals seeking...Read more
Bioavailability of drugs is a key factor in determining the efficacy of a drug. It refers to the degree and rate at which a drug is absorbed and made available to the target tissue or organs. In this article, we will discuss the concept of bioavailability, its importance and factors that influence it. We will also discuss the various ways of measuring bioavailability and its implications for drug delivery.
Bioavailability of Drug is a measure of how much of the drug enters the bloodstream after being taken orally. It is determined by how much of the drug is absorbed from the gut into the bloodstream, and how fast it is delivered to the target organs. Factors that affect bioavailability include the drug’s solubility, the route of administration, and the individual’s metabolism. Bioavailability is also affected by the drug’s formulation, such as if it is taken as a pill, syrup, or injectable. In general, drugs with higher bioavailability are more effective, as they are delivered to the target organs faster and can be used in lower doses.
Contents
- Definition of Drug Bioavailability
- Factors Affecting Drug Bioavailability
- Measuring Drug Bioavailability
- The Importance of Drug Bioavailability
- Top 6 Frequently Asked Questions
- What is Bioavailability of Drug?
- What Factors Affect the Bioavailability of Drugs?
- What is the Difference Between Bioavailability and Bioequivalence?
- How is Bioavailability Measured?
- What is the Role of Bioavailability in Drug Development?
- What is the Difference Between Absolute and Relative Bioavailability?
- Is Diethylpropion A Stimulant?
- Is Alcohol A Inflammatory?
- Does Alcohol Make A Uti Worse?
Definition of Drug Bioavailability
Drug bioavailability is the amount of a drug that is available to the body for use, often measured in terms of the drug’s concentration in the bloodstream or tissues. It is a measure of the rate and extent to which a drug is absorbed into the bloodstream and reaches its site of action. The bioavailability of a drug depends on several factors, such as the type of drug, route of administration, and other physiological characteristics.
Bioavailability is an important consideration when determining the efficacy of a drug. It is also used to determine the dosage of a drug that is required to achieve the desired therapeutic effect. Bioavailability can be affected by a variety of factors, including the formulation of the drug, route of administration, and patient characteristics.
Factors Affecting Drug Bioavailability
Drug bioavailability is affected by a variety of factors, including the formulation of the drug, the route of administration, and patient characteristics. The formulation of the drug is one of the most important factors affecting bioavailability. The formulation of the drug determines how much of the drug is absorbed and how quickly it is absorbed. Different formulations of a drug may have different bioavailability, so it is important to select the formulation that will provide optimal bioavailability.
The route of administration also affects the bioavailability of a drug. Different routes of administration may result in different levels of bioavailability. For example, oral administration of a drug may result in less bioavailability than intravenous administration. Additionally, the speed of absorption of a drug can vary depending on the route of administration.
Patient characteristics, such as age, gender, and health status, may also affect the bioavailability of a drug. For example, elderly patients may have reduced bioavailability due to changes in drug metabolism. Additionally, certain drugs may interact with other drugs or dietary components, which can affect their bioavailability.
Measuring Drug Bioavailability
Drug bioavailability can be measured in a variety of ways. The most common method is to measure the concentration of the drug in the blood or tissues. This method is often used to compare the bioavailability of different formulations of the same drug.
Another method of measuring bioavailability is to measure the rate of drug absorption. This is done by calculating the amount of drug that is absorbed over a certain period of time. This method is often used for drugs that are slowly absorbed, such as those that are administered orally.
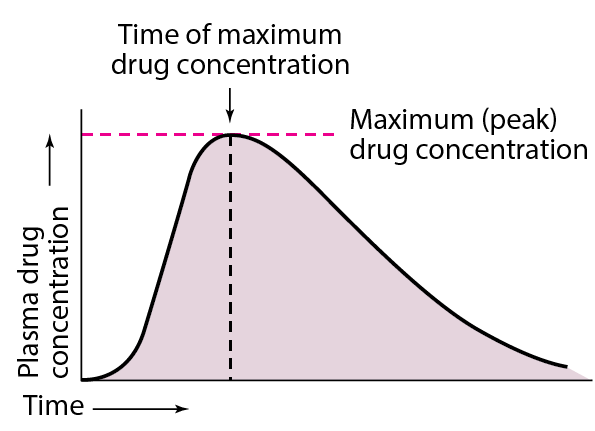
Finally, the extent of drug bioavailability can also be measured by calculating the area under the concentration-time curve (AUC). This method is used to compare the bioavailability of different formulations of the same drug, as well as different routes of administration.
The Importance of Drug Bioavailability
Drug bioavailability is an important consideration when determining the efficacy of a drug. It is also used to determine the dosage of a drug that is required to achieve the desired therapeutic effect. Bioavailability can be affected by a variety of factors, including the formulation of the drug, route of administration, and patient characteristics. Therefore, it is important to select the formulation and route of administration that will provide optimal bioavailability. Additionally, understanding the factors that affect bioavailability can help to improve the efficacy of a drug.
Top 6 Frequently Asked Questions
What is Bioavailability of Drug?
Answer: Bioavailability is the degree and rate at which a drug or other substance is absorbed into the bloodstream and is available for use by the body’s cells and tissues. The bioavailability of a drug or other substance is determined by the dose taken, the form of the drug or substance, and the route by which it is administered, among other factors. Bioavailability is an important factor in determining the effectiveness of a drug or other substance.
What Factors Affect the Bioavailability of Drugs?
Answer: The bioavailability of a drug or other substance is determined by a variety of factors, including the dose taken, the form of the drug or substance, and the route by which it is administered. Other factors that can affect bioavailability include the drug’s solubility, the pH of the body’s fluids, the presence of other drugs or substances in the body, and the speed at which a drug is metabolized.
What is the Difference Between Bioavailability and Bioequivalence?
Answer: Bioavailability is the degree and rate at which a drug or other substance is absorbed into the bloodstream, while bioequivalence is the degree to which two different formulations of the same drug have the same pharmacological effect in the body. Bioequivalence is determined through clinical studies that compare the rate and extent of absorption of two formulations of the same drug.
How is Bioavailability Measured?
Answer: Bioavailability can be measured through a variety of methods, including pharmacokinetic studies, in vivo studies, in vitro studies, and animal models. Pharmacokinetic studies measure the rate and extent of absorption of a drug or other substance, while in vivo studies measure the effects of the drug on living organisms. In vitro studies measure the amount of the drug or substance that is absorbed into the bloodstream, and animal models measure the effects of a drug on a specific animal species.
What is the Role of Bioavailability in Drug Development?
Answer: Bioavailability plays an important role in drug development, as it helps pharmaceutical companies to determine the effectiveness of a drug and to refine the drug’s formulation and delivery systems. By understanding the bioavailability of a drug, pharmaceutical companies can improve the drug’s efficacy and minimize side effects.
What is the Difference Between Absolute and Relative Bioavailability?
Answer: Absolute bioavailability is the fraction of an administered dose of a drug that is absorbed into the systemic circulation and is available for use by the body’s cells and tissues. Relative bioavailability is a measure of how the bioavailability of a drug compares to that of an intravenous or oral reference formulation of the same drug. Relative bioavailability is generally expressed as a percentage.
In conclusion, the bioavailability of a drug is a critical factor in its effectiveness. It is a measure of how much of the active drug is available to the body. Depending on the type of drug, different factors can impact its bioavailability, such as the route of administration, dosage form, and metabolic enzymes. To ensure the maximum effectiveness of a drug, it is important to consider all of these factors when prescribing it.
Francisco Church is a rehabilitation specialist and the chief editor of Recovery Ranger. He creates this site to offer guidance and support to individuals seeking to overcome addiction and achieve lasting sobriety. With extensive experience in the field of addiction treatment, Francisco is dedicated to helping individuals access the resources they need for successful recovery.
- Latest Posts by Francisco Church
-
Is Diethylpropion A Stimulant?
- -
Is Alcohol A Inflammatory?
- -
Does Alcohol Make A Uti Worse?
- All Posts