Francisco Church is a rehabilitation specialist and the chief editor of Recovery Ranger. He creates this site to offer guidance and support to individuals seeking...Read more
Addictive drugs are a major problem in many societies today, leading to physical and mental health issues, financial problems, and even death. But what exactly is an addictive drug? In this article, we will explore the definition of an addictive drug, its effects on the body, and the potential treatments available. Readers will gain an understanding of the risks associated with these substances, and the importance of taking action to prevent and treat addiction.
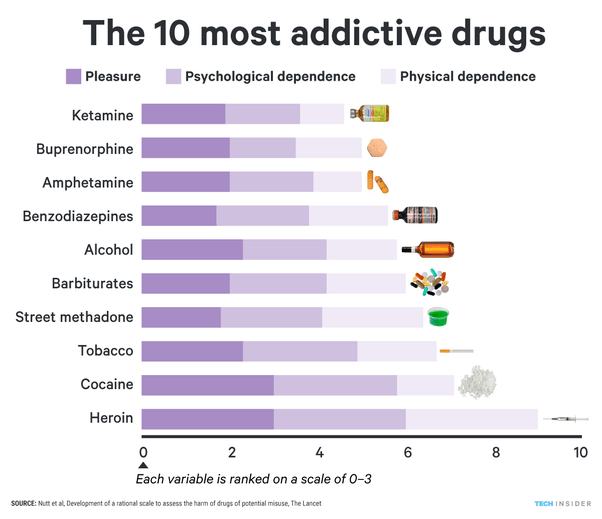
An addictive drug is a drug that causes physical or psychological dependence. Examples of addictive drugs include heroin, cocaine, alcohol, opioid painkillers, and nicotine. These drugs can cause intense cravings and changes in the brain that make it difficult to stop using them.
When someone is addicted to a drug, cravings and withdrawal symptoms occur when they attempt to stop taking the drug. Common withdrawal symptoms include anxiety, insomnia, nausea, and sweating. Treatment for an addiction to drugs often involves counseling, therapy, and medications to help the person manage cravings and withdrawal symptoms.
Contents
- What is an Addiction-Causing Drug?
- Types of Addictive Drugs
- Signs and Symptoms of Drug Addiction
- Treatment for Drug Addiction
- Few Frequently Asked Questions
- What is an Addictive Drug?
- What are the Different Types of Addictive Drugs?
- What are the Signs of Drug Addiction?
- What are the Effects of Drug Addiction?
- What are the Treatments for Drug Addiction?
- What are the Consequences of Drug Addiction?
- Mechanism of Drug Addiction in the Brain, Animation.
- Is Diethylpropion A Stimulant?
- Is Alcohol A Inflammatory?
- Does Alcohol Make A Uti Worse?
What is an Addiction-Causing Drug?
Addictive drugs are chemical substances that change the way the brain works. They affect the central nervous system and can lead to physical and psychological dependence. These drugs include prescription medicines, illegal drugs, and over-the-counter medicines. The most common addictive drugs are alcohol, nicotine, opioids, and benzodiazepines.
Addictive drugs act on the brain’s reward system, causing a release of dopamine and other neurotransmitters. This release of neurotransmitters creates a sense of euphoria or pleasure. Over time, the brain may become accustomed to the effects of the drug and crave more of it. It is this craving that leads to addiction.
Addictive drugs can cause physical and psychological dependence. Physical dependence occurs when the body needs the drug to function normally. Psychological dependence occurs when the user needs the drug to feel pleasure or to cope with daily life.
Types of Addictive Drugs
Alcohol is one of the most commonly abused addictive drugs. It acts on the brain’s reward system and can lead to physical and psychological dependence. Long-term alcohol use can lead to liver damage and other health problems.
Nicotine is another commonly abused addictive drug. It is found in cigarettes, chewing tobacco, and e-cigarettes. Nicotine acts on the brain’s reward system and can lead to physical and psychological dependence. Long-term nicotine use can lead to cancer, heart disease, and other health problems.
Opioids are a class of drugs that act on the brain’s reward system and can lead to physical and psychological dependence. Common opioids include heroin, fentanyl, and prescription painkillers. Long-term opioid use can lead to addiction, overdose, and death.
Benzodiazepines are a class of drugs that act on the brain’s reward system and can lead to physical and psychological dependence. Common benzodiazepines include Xanax and Valium. Long-term benzodiazepine use can lead to addiction, memory problems, and other health problems.
Signs and Symptoms of Drug Addiction
Using drugs for a long period of time or using more than prescribed can lead to addiction. Common signs and symptoms of addiction include:
Cravings
A strong need or urge to use the drug.
Loss of Control
Using more of the drug than planned, or continuing to use the drug despite negative consequences.
Risky Behavior
Engaging in dangerous activities while under the influence of drugs.
Treatment for Drug Addiction
Treatment for drug addiction typically involves a combination of therapy and medication. Therapy can help the person learn new skills to cope with stress and cravings. Medication can help to manage cravings and withdrawal symptoms.
Behavioral Therapy
Behavioral therapy can help a person identify triggers, develop new coping skills, and manage cravings.
Medication-Assisted Treatment
Medication-assisted treatment (MAT) combines therapy with medication to help treat drug addiction. Common medications used in MAT include methadone, buprenorphine, and naltrexone.
Few Frequently Asked Questions
What is an Addictive Drug?
An addictive drug is a substance that causes physical or psychological dependence. It can lead to compulsive drug-seeking behavior, even in the face of negative consequences. These drugs can be legal, such as alcohol, or illegal, such as cocaine.
What are the Different Types of Addictive Drugs?
Addictive drugs can be divided into three broad categories: stimulants, depressants, and hallucinogens. Stimulants, such as cocaine and amphetamines, act on the central nervous system to increase alertness, energy, and wakefulness. Depressants, such as alcohol, barbiturates, and opioids, slow down brain activity and can produce a calming effect. Hallucinogens, such as LSD and ecstasy, produce changes in perception, mood, and emotion.
What are the Signs of Drug Addiction?
The signs of drug addiction can vary depending on the drug, but generally include a strong craving for the drug, difficulty stopping its use, and negative consequences from its use. Other signs can include changes in behavior, such as increased irritability and hostility, decreased interest in activities, and changes in sleep patterns.
What are the Effects of Drug Addiction?
The effects of drug addiction can be both physical and psychological. Physically, addiction can cause changes in the body, such as an increased risk of developing various diseases, organ damage, and even death. Psychologically, addiction can cause changes in mood, behavior, and thinking. It can also lead to feelings of guilt, shame, and anxiety, as well as impaired judgment.
What are the Treatments for Drug Addiction?
The treatments for drug addiction vary depending on the individual and the drug involved, but generally include some combination of counseling, therapy, and medication. Counseling and therapy can provide techniques and strategies to help the individual cope with their addiction, while medications such as antidepressants and anti-anxiety drugs can help to reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms.
What are the Consequences of Drug Addiction?
The consequences of drug addiction can be both short-term and long-term. In the short-term, addiction can lead to serious health problems, loss of job and relationships, and legal issues. In the long-term, addiction can lead to further health problems, financial problems, and an increased risk of death.
Mechanism of Drug Addiction in the Brain, Animation.
In conclusion, addiction to drugs is a serious problem that affects society. Addictive drugs are those that cause physical and psychological dependence, leading to a range of health and social problems. While there is no one definition of an addictive drug, the most commonly used definition includes those that cause dependence, lead to compulsive use and interfere with normal functioning. Addictive drugs can be both legal and illegal, and should be avoided as much as possible.
Francisco Church is a rehabilitation specialist and the chief editor of Recovery Ranger. He creates this site to offer guidance and support to individuals seeking to overcome addiction and achieve lasting sobriety. With extensive experience in the field of addiction treatment, Francisco is dedicated to helping individuals access the resources they need for successful recovery.
- Latest Posts by Francisco Church
-
Is Diethylpropion A Stimulant?
- -
Is Alcohol A Inflammatory?
- -
Does Alcohol Make A Uti Worse?
- All Posts