Francisco Church is a rehabilitation specialist and the chief editor of Recovery Ranger. He creates this site to offer guidance and support to individuals seeking...Read more
Nicotine is one of the most widely used and addictive substances in the world today. It is the main psychoactive component of tobacco, and it is used in various forms, including cigarettes, cigars, chewing tobacco, and electronic cigarettes. But what effect does nicotine have on the brain? This article looks at the neurological effects of nicotine, from how it affects the brain’s chemistry to how it can lead to dependence.
Contents
- Nicotine and its Effects on the Brain
- Few Frequently Asked Questions
- What is Nicotine?
- What are the Effects of Nicotine on the Brain?
- How Does Nicotine Addiction Develop?
- What are the Long-term Effects of Nicotine on the Brain?
- What are the Signs of Nicotine Addiction?
- What are the Best Ways to Quit Smoking?
- Vaping: The Hit Your Brain Takes
- Is Diethylpropion A Stimulant?
- Is Alcohol A Inflammatory?
- Does Alcohol Make A Uti Worse?
Nicotine and its Effects on the Brain
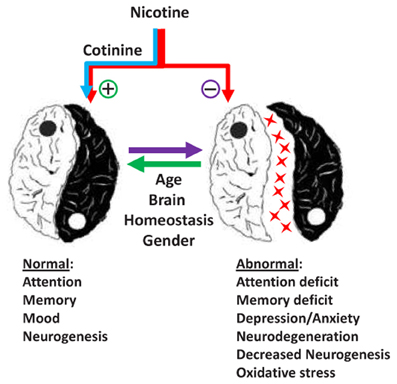
Nicotine is a drug found in tobacco products that is highly addictive. It can have both short-term and long-term effects on the brain. In this article, we will explore the effects of nicotine on the brain and how it affects cognitive functioning.
Short-term Effects of Nicotine on the Brain
When nicotine enters the body, it reaches the brain within seconds and binds to nicotine receptors. This causes the release of neurotransmitters such as dopamine, which make the user feel relaxed and alert. Nicotine also increases the amount of noradrenaline, which helps to improve concentration and alertness. This can lead to improved performance on tasks that require focus and concentration.
However, nicotine also has some negative effects on the brain. It can increase the risk of anxiety, depression, and other mental health issues. It can also impair memory and learning, and cause difficulty in problem-solving. In addition, nicotine can lead to increased aggression and can have a negative impact on impulse control.
Long-term Effects of Nicotine on the Brain
Long-term use of nicotine can lead to physical changes in the brain. Regular exposure to nicotine can lead to a decrease in the number of receptors that respond to the drug. This can lead to changes in brain chemistry and an increased tolerance to nicotine, making it harder to quit.
Long-term nicotine use can also lead to changes in the brain’s reward system. This can lead to increased cravings for nicotine and a greater likelihood of developing an addiction. It can also lead to an increased risk of cognitive decline and an increased risk of developing dementia and other age-related cognitive disorders.
Nicotine Replacement Therapy
Nicotine replacement therapy (NRT) is a method of treating nicotine addiction. It involves using nicotine-containing products such as patches, gum, and inhalers, to reduce the amount of nicotine in the body and gradually reduce cravings. NRT can help to reduce the short- and long-term effects of nicotine on the brain, and can help to reduce the risk of developing an addiction.
Quitting Smoking and Nicotine Use
Quitting smoking and nicotine use can have a positive effect on the brain. Quitting can lead to improved cognitive functioning, improved memory and learning, and a reduced risk of depression and anxiety. It can also reduce the risk of developing dementia and other age-related cognitive disorders.
Conclusion
Nicotine has both short-term and long-term effects on the brain. In the short-term, it can lead to improved focus and concentration, but can also lead to increased anxiety and depression. In the long-term, it can lead to changes in brain chemistry and an increased risk of developing an addiction. Nicotine replacement therapy can be used to reduce the effects of nicotine on the brain, and quitting smoking and nicotine use can have a positive effect on cognitive functioning.
Few Frequently Asked Questions
What is Nicotine?
Nicotine is a naturally occurring chemical found in tobacco and certain other plants. It is a stimulant that produces a feeling of alertness and well-being when it is consumed. It is also highly addictive, and it can be found in cigarettes, cigars, chewing tobacco, and many other products. Nicotine can also be consumed in liquid form, such as in e-cigarettes and vape pens.
What are the Effects of Nicotine on the Brain?
Nicotine has a significant effect on the brain. It stimulates the release of neurotransmitters such as dopamine and norepinephrine, which can produce a feeling of pleasure and reward. It can also increase alertness and concentration, and it has been linked to improved memory and learning. Nicotine can also cause the release of epinephrine and cortisol, which can lead to increased heart rate and blood pressure.
How Does Nicotine Addiction Develop?
Nicotine addiction is a serious issue and can develop quickly. It occurs as the brain becomes accustomed to the presence of nicotine and starts to rely on it for stimulation. As a result, withdrawal symptoms can occur when nicotine is no longer present, and these can be unpleasant and difficult to manage.
What are the Long-term Effects of Nicotine on the Brain?
The long-term effects of nicotine on the brain can be severe. Chronic nicotine use can lead to an increased risk of stroke, heart attack and other cardiovascular diseases. Additionally, nicotine can cause changes in the brain that can lead to cognitive and behavioral problems, such as difficulty concentrating and increased impulsivity. It can also damage the cells that create and maintain short-term memory, resulting in memory loss.
What are the Signs of Nicotine Addiction?
Signs of nicotine addiction can vary from person to person, but some common signs include an increase in the amount of nicotine required to achieve the desired effect, cravings for nicotine, withdrawal symptoms when nicotine is not available, and difficulty quitting or reducing nicotine consumption. Additionally, nicotine addiction can lead to psychological and physical dependence, as well as an increase in tolerance.
What are the Best Ways to Quit Smoking?
Quitting smoking can be difficult, but there are many resources available to help. Quitlines, such as 1-800-QUIT-NOW, can provide free counseling and support. Additionally, nicotine replacement therapy, such as patches and gum, can reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms. Other methods, such as counseling, support groups, and prescription medications, can also be beneficial. It is important to remember that quitting smoking is a process, and it may take multiple attempts before it is successful.
Vaping: The Hit Your Brain Takes
To conclude, nicotine has a major effect on the brain. It can lead to increased heart rate and blood pressure, increased alertness and concentration, and increased pleasure and reward responses. It can also lead to increased risk of addiction, cognitive deficits, and increased risk of certain diseases. While nicotine may have some beneficial effects on the brain, it is important to understand the risks associated with nicotine use and to take steps to reduce its harmful effects.
Francisco Church is a rehabilitation specialist and the chief editor of Recovery Ranger. He creates this site to offer guidance and support to individuals seeking to overcome addiction and achieve lasting sobriety. With extensive experience in the field of addiction treatment, Francisco is dedicated to helping individuals access the resources they need for successful recovery.
- Latest Posts by Francisco Church
-
Is Diethylpropion A Stimulant?
- -
Is Alcohol A Inflammatory?
- -
Does Alcohol Make A Uti Worse?
- All Posts