Francisco Church is a rehabilitation specialist and the chief editor of Recovery Ranger. He creates this site to offer guidance and support to individuals seeking...Read more
Ecstasy is a complex drug with a complex reputation, and many people are unsure of where it stands in terms of its effects. Is it a stimulant, a depressant, or something else entirely? In this article, we will explore the science behind ecstasy and answer the question – is ecstasy a stimulant or a depressant?
Contents
- Ecstasy is a Synthetic Stimulant Drug
- Ecstasy is Not a Depressant Drug
- Ecstasy is a synthetic Stimulant Drug
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
- What is Ecstasy?
- Is Ecstasy a Stimulant or a Depressant?
- What Are the Effects of Taking Ecstasy?
- What are the Risks of Taking Ecstasy?
- Can Ecstasy be Addictive?
- What is the Best Treatment for Ecstasy Addiction?
- Drug Awareness: Depressants, Hallucinogens And Stimulants
- Is Diethylpropion A Stimulant?
- Is Alcohol A Inflammatory?
- Does Alcohol Make A Uti Worse?
Ecstasy is a Synthetic Stimulant Drug
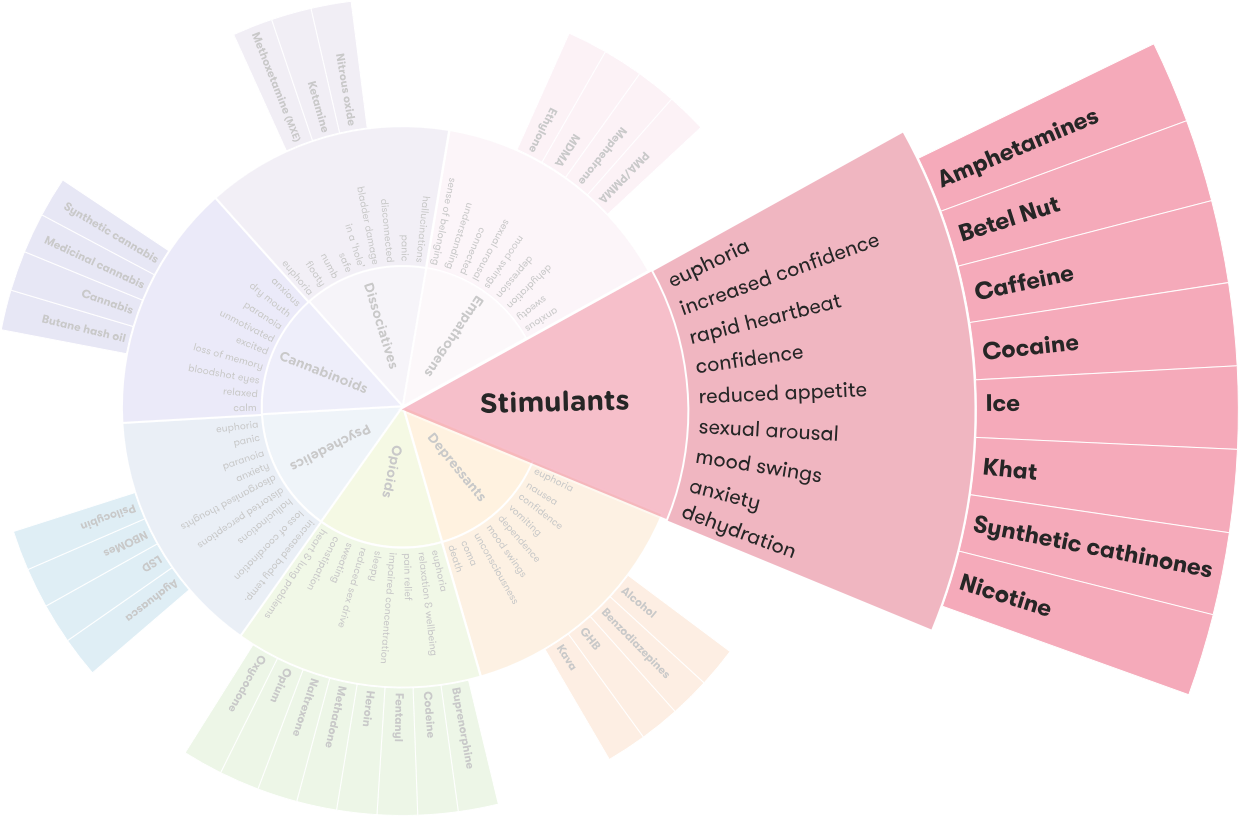
Ecstasy, or MDMA, is a synthetic stimulant drug that is primarily used recreationally. It is commonly known as “molly” or “e,” and it is often found in pill or powder form. Although it is sometimes referred to as an “upper” or a “downer,” ecstasy is technically classified as a stimulant. When taken, the drug triggers the release of serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine in the brain, which can produce feelings of euphoria, increased energy, and heightened sensations.
Short-Term Effects of Ecstasy
The primary effect of ecstasy is an intense feeling of euphoria and pleasure, which can last for several hours. Other short-term effects of the drug include increased energy, feelings of closeness and empathy with others, and an overall sense of well-being. Ecstasy can also increase alertness, focus, and the ability to concentrate. However, the drug can also cause a range of adverse effects, including increased heart rate, dehydration, and anxiety.
Long-Term Effects of Ecstasy
The long-term effects of ecstasy are not yet fully understood, although there is evidence to suggest that the drug can cause significant damage to the brain. Regular use of ecstasy has been linked to changes in cognitive abilities, memory problems, and depression. It may also lead to an increased risk of developing mental health conditions such as anxiety and psychosis. Additionally, ecstasy can cause physical harm, including liver and kidney damage.
Ecstasy is Not a Depressant Drug
Ecstasy is not a depressant drug, despite the fact that it can cause feelings of depression and anxiety. This is due to the fact that ecstasy is a stimulant drug, meaning that it increases the activity of the central nervous system. In contrast, depressants are drugs that slow down the activity of the central nervous system, resulting in feelings of relaxation and sedation.
The Misconception that Ecstasy is a Depressant
The misconception that ecstasy is a depressant drug is likely due to the fact that it can produce feelings of depression and anxiety in some users. Additionally, some people may confuse the drug with other depressant drugs, such as alcohol and benzodiazepines. It is important to remember that, despite its effects, ecstasy is a stimulant drug, not a depressant.
Risks Associated with Ecstasy
Although ecstasy is not a depressant drug, it can still cause a range of adverse effects. As with any drug, it is important to be aware of the potential risks associated with ecstasy use. These can include increased heart rate, dehydration, anxiety, depression, memory problems, and an increased risk of developing mental health conditions. Additionally, regular use of the drug can lead to physical harm, including liver and kidney damage.
Ecstasy is a synthetic Stimulant Drug
Ecstasy, or MDMA, is a synthetic stimulant drug that is primarily used recreationally. It is commonly known as “molly” or “e,” and it is often found in pill or powder form. Although it is sometimes referred to as an “upper” or a “downer,” ecstasy is technically classified as a stimulant. When taken, the drug triggers the release of serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine in the brain, which can produce feelings of euphoria, increased energy, and heightened sensations.
The Effects of Ecstasy
The primary effect of ecstasy is an intense feeling of euphoria and pleasure, which can last for several hours. Other short-term effects of the drug include increased energy, feelings of closeness and empathy with others, and an overall sense of well-being. Ecstasy can also increase alertness, focus, and the ability to concentrate. However, the drug can also cause a range of adverse effects, including increased heart rate, dehydration, and anxiety.
Long-Term Effects of Ecstasy
The long-term effects of ecstasy are not yet fully understood, although there is evidence to suggest that the drug can cause significant damage to the brain. Regular use of ecstasy has been linked to changes in cognitive abilities, memory problems, and depression. It may also lead to an increased risk of developing mental health conditions such as anxiety and psychosis. Additionally, ecstasy can cause physical harm, including liver and kidney damage.
Conclusion
Ecstasy is a synthetic stimulant drug that is primarily used recreationally. Its primary effects include an intense feeling of euphoria and pleasure, as well as increased energy, alertness, and focus. However, the drug can also cause a range of adverse effects, including increased heart rate, dehydration, and anxiety. Additionally, regular use of ecstasy has been linked to changes in cognitive abilities, memory problems, and depression. It is important to remember that, despite its effects, ecstasy is a stimulant drug, not a depressant.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Ecstasy?
Ecstasy is a psychoactive drug, often referred to as a stimulant or hallucinogenic. It is also known by its scientific name, MDMA (3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine). It is most commonly found in pill form, but can also be found in powder or crystal form. Ecstasy acts on the brain’s serotonin receptors, producing feelings of euphoria, increased energy and heightened sensory perceptions.
Is Ecstasy a Stimulant or a Depressant?
Ecstasy is considered a stimulant, as it can produce feelings of alertness, energy and euphoria. These effects can last for several hours and can be very intense. However, ecstasy can also have some depressant effects, as it can reduce inhibitions and make it difficult to concentrate.
What Are the Effects of Taking Ecstasy?
The effects of taking ecstasy can vary greatly, depending on the individual’s genetic makeup and their environment. Common short-term effects include increased energy, heightened sensory perception, feelings of euphoria, increased heart rate, and increased sociability. Long-term effects of ecstasy use can include anxiety, depression, memory loss, and confusion.
What are the Risks of Taking Ecstasy?
The risks of taking ecstasy are numerous, and can range from mild to severe. Short-term risks include dehydration, overheating, and seizures. Long-term risks of ecstasy use include depression, memory loss, confusion, and serious mental health issues. Ecstasy can also be cut with other drugs, making it difficult to know what one is taking and further increasing the risk of overdose.
Can Ecstasy be Addictive?
Yes, ecstasy can be addictive. Regular use of ecstasy can lead to tolerance, meaning that more and more of the drug is needed to achieve the same effects. Additionally, long-term use of ecstasy can lead to physical and psychological dependence, making it difficult to quit without professional help.
What is the Best Treatment for Ecstasy Addiction?
The best treatment for ecstasy addiction is a comprehensive approach that includes both medical and psychological treatment. Medical treatment may involve medications to help reduce withdrawal symptoms and cravings, while psychological treatment may involve cognitive-behavioral therapy, 12-step programs, and other evidence-based approaches. Additionally, support from family and friends can help those struggling with addiction to maintain sobriety and live a healthy, productive life.
Drug Awareness: Depressants, Hallucinogens And Stimulants
In conclusion, it is evident that the classification of Ecstasy as either a stimulant or a depressant is not straightforward. While it may have the ability to act as both a stimulant and a depressant, its effects are highly dependent on the individual and the amount consumed. Therefore, it is important to have an informed understanding of the drug before taking it.
Francisco Church is a rehabilitation specialist and the chief editor of Recovery Ranger. He creates this site to offer guidance and support to individuals seeking to overcome addiction and achieve lasting sobriety. With extensive experience in the field of addiction treatment, Francisco is dedicated to helping individuals access the resources they need for successful recovery.
- Latest Posts by Francisco Church
-
Is Diethylpropion A Stimulant?
- -
Is Alcohol A Inflammatory?
- -
Does Alcohol Make A Uti Worse?
- All Posts