Francisco Church is a rehabilitation specialist and the chief editor of Recovery Ranger. He creates this site to offer guidance and support to individuals seeking...Read more
Alcohols are widely used in many industries, from pharmaceuticals to food production. But have you ever wondered if alcohol is hydrophobic? In this article, we will explore the properties of alcohol and how they affect its hydrophobicity. We will discuss the different types of alcohols, their structure and properties, and how they interact with water molecules. Finally, we will consider how this affects the use of alcohol in various industries and applications. So let’s dive in and find out if alcohol is hydrophobic or not!
Contents
- What is Hydrophobicity?
- Conclusion
- Top 6 Frequently Asked Questions
- Question 1: What is Alcohol?
- Question 2: What is Hydrophobic?
- Question 3: Is Alcohol Hydrophobic?
- Question 4: How does Alcohol React with Water?
- Question 5: What is Hydrophilic?
- Question 6: What are the Properties of Hydrophobic Molecules?
- Pandemic Drinking: Why is Alcohol so Dehydrating?
- Is Diethylpropion A Stimulant?
- Is Alcohol A Inflammatory?
- Does Alcohol Make A Uti Worse?
What is Hydrophobicity?
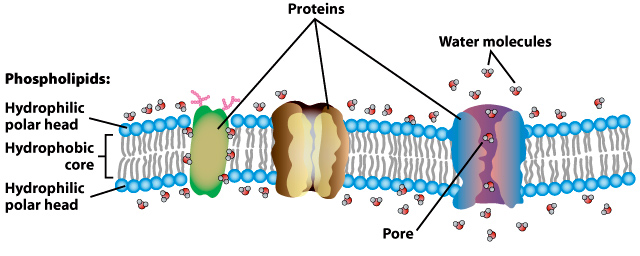
Hydrophobicity is the property of a substance that repels water. It can be measured in terms of the strength of the repulsion, which is typically measured on a scale from one to 10, with 10 being the strongest. Hydrophobicity is an important concept in biology and materials science, as it affects the way that molecules interact with each other in aqueous solutions. It is also used to describe the behavior of non-polar molecules in aqueous solutions.
In biology, hydrophobicity is important in the formation of cell membranes and in the folding of proteins. In materials science, hydrophobicity is used to describe the behavior of non-polar molecules in aqueous solutions, such as oils and waxes.
What is Alcohol?
Alcohol is a chemical compound that is composed of a hydroxyl group (-OH) attached to an alkyl group (a carbon chain). Alcohols can be divided into two broad categories: primary alcohols, which have a single hydroxyl group, and secondary alcohols, which have two hydroxyl groups. Alcohols are found in a variety of products, from alcoholic beverages to industrial solvents.
Alcohols are known for their ability to dissolve other compounds, including lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates. This is due to the presence of the hydroxyl group, which has a slightly negative charge and forms hydrogen bonds with other molecules.
Is Alcohol Hydrophobic?
Alcohol is generally considered to be hydrophobic, meaning that it does not interact strongly with water molecules. This is due to the presence of the hydroxyl group, which is slightly negatively charged and thus repels water molecules.
However, alcohols can also be hydrophilic, depending on the structure of the molecule. For example, alcohols with two or more hydroxyl groups can form hydrogen bonds with water molecules and become hydrophilic.
How Does Alcohol Interact with Water?
Alcohols typically interact with water molecules through hydrogen bonds, which are formed between the slightly negative charge of the hydroxyl group and the slightly positive charge of the water molecule. This interaction creates a weak bond between the two molecules, which does not affect the structure of the water molecule.
The interaction between alcohol and water molecules can also be affected by the presence of other molecules. For example, alcohols can form stronger hydrogen bonds with certain solutes such as salts or sugars, which can make the alcohol more hydrophilic.
What Are the Applications of Hydrophobicity?
Hydrophobicity is an important property in many biological and chemical processes. In biology, hydrophobicity is important for the formation of cell membranes and the folding of proteins. In materials science, hydrophobicity is used to describe the behavior of non-polar molecules in aqueous solutions, such as oils and waxes.
Hydrophobicity can also be used to create materials with specific properties. For example, hydrophobic materials can be used to coat surfaces to make them water-resistant, or to create materials that repel water.
Conclusion
In conclusion, alcohol is generally considered to be hydrophobic, meaning that it does not interact strongly with water molecules. However, the interaction between alcohol and water molecules can be affected by the presence of other molecules, such as salts or sugars. Hydrophobicity is an important property in many biological and chemical processes, and can be used to create materials with specific properties.
Top 6 Frequently Asked Questions
Question 1: What is Alcohol?
Answer: Alcohol is an organic compound composed of a hydrocarbon group and one or more hydroxyl groups. It is a type of alcohol that is commonly used in beverages and other products. There are many different types of alcohol, such as ethyl alcohol, methyl alcohol, and isopropyl alcohol. Ethyl alcohol is the type of alcohol typically found in alcoholic beverages.
Question 2: What is Hydrophobic?
Answer: Hydrophobic molecules are molecules that are not attracted to water and tend to repel it. This is due to the fact that they are composed of non-polar molecules that are not easily soluble in water. Examples of hydrophobic molecules include oil, waxes, fats, and alcohol.
Question 3: Is Alcohol Hydrophobic?
Answer: Yes, alcohol is a hydrophobic molecule. This is because it is composed of non-polar molecules that are not easily soluble in water. Alcohols are typically insoluble in water and tend to repel it.
Question 4: How does Alcohol React with Water?
Answer: Alcohols are generally insoluble in water, meaning that they don’t mix with water and tend to repel it. When alcohol and water are mixed together, the alcohol molecules form a separate layer on top of the water. This is because of the hydrophobic nature of alcohol.
Question 5: What is Hydrophilic?
Answer: Hydrophilic molecules are molecules that are attracted to water and easily soluble in water. This is due to the fact that they are composed of polar molecules that are easily soluble in water. Examples of hydrophilic molecules include table salt, sugar, and detergents.
Question 6: What are the Properties of Hydrophobic Molecules?
Answer: Hydrophobic molecules are molecules that are not attracted to water and tend to repel it. This is due to the fact that they are composed of non-polar molecules that are not easily soluble in water. These molecules tend to form a separate layer on top of the water due to their hydrophobic nature. Examples of hydrophobic molecules include oil, waxes, fats, and alcohols.
Pandemic Drinking: Why is Alcohol so Dehydrating?
It is clear that the answer to the question of whether alcohol is hydrophobic or not is a complex one. While it is true that alcohol molecules are not attracted to water molecules, it is also true that in certain concentrations alcohol can interact with water molecules and even dissolve in water. This complexity further emphasizes the need for further research into the hydrophobic properties of alcohol.
Francisco Church is a rehabilitation specialist and the chief editor of Recovery Ranger. He creates this site to offer guidance and support to individuals seeking to overcome addiction and achieve lasting sobriety. With extensive experience in the field of addiction treatment, Francisco is dedicated to helping individuals access the resources they need for successful recovery.
- Latest Posts by Francisco Church
-
Is Diethylpropion A Stimulant?
- -
Is Alcohol A Inflammatory?
- -
Does Alcohol Make A Uti Worse?
- All Posts