Francisco Church is a rehabilitation specialist and the chief editor of Recovery Ranger. He creates this site to offer guidance and support to individuals seeking...Read more
Opioid addiction is a growing problem in our society. According to the National Institute of Drug Abuse, an estimated 2.1 million people in the United States are currently suffering from an opioid addiction. The opioid crisis is a serious issue that affects not only those addicted to opioids, but also their families, friends, and communities. In this article, we will explore the scope of the opioid crisis, how it has affected people in the United States, and what can be done to help those in need. We will discuss how many people are addicted to opioids, the factors that contribute to opioid addiction, and the treatment options available.
Contents
- Overview of Opioid Addiction in the United States
- Who Is at Risk for Opioid Addiction?
- Treatment and Prevention of Opioid Addiction
- Conclusion
- Top 6 Frequently Asked Questions
- What Is an Opioid?
- What Is Opioid Addiction?
- How Many People Are Addicted to Opioids?
- What Are the Effects of Opioid Addiction?
- Are There Any Treatments for Opioid Addiction?
- What Can I Do to Help Someone with an Opioid Addiction?
- Descent into opioid addiction captured on video
- Is Diethylpropion A Stimulant?
- Is Alcohol A Inflammatory?
- Does Alcohol Make A Uti Worse?
Overview of Opioid Addiction in the United States
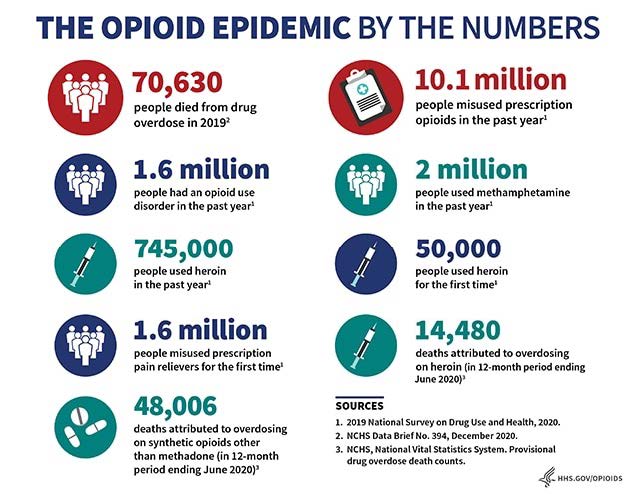
Opioids are a type of drug that is commonly used to treat pain, and they are highly addictive. In the United States, opioid addiction has become a major public health concern due to its widespread use and abuse. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), more than 130 people die each day due to opioid-related overdoses. The opioid crisis has become one of the most pressing public health issues in the US, and it is estimated that over 10 million people are addicted to opioids.
The opioid epidemic has been fueled by the overprescription of opioids, the increased availability of illicit opioids, and the lack of access to treatment and prevention services. In 2019, the US Department of Health and Human Services reported that there were more than 2 million people in the US with a substance use disorder related to opioids. It is estimated that around 11.5 million people misused opioids in 2019, and it is estimated that around 886,000 people had a severe opioid use disorder.
Who Is at Risk for Opioid Addiction?
Opioid addiction affects people from all walks of life and all ages. However, certain individuals are more at risk for developing an addiction to opioids than others. People who are already struggling with mental health issues, such as depression and anxiety, are more likely to become addicted to opioids, as are people with a history of substance abuse. People who are younger and those who are exposed to opioids through friends or family members are also more likely to become addicted.
Additionally, people who have chronic pain conditions, such as arthritis or back pain, are also at a higher risk of developing an opioid addiction. This is due to the fact that they may take opioids for an extended period of time, increasing their chances of becoming addicted. People who have been prescribed opioids for a long time may also become dependent on the drug, as the body can become accustomed to the effects of the drug and require it to function normally.
Prescription Opioids and Addiction
Prescription opioids are one of the most commonly abused drugs in the US, and they are one of the leading contributors to the opioid epidemic. A 2019 study from the CDC found that around 66% of opioid-related deaths involved a prescription opioid. Prescription opioids can be highly addictive, and they can be abused in several ways, including snorting, smoking, or injecting them.
Prescription opioids can be incredibly dangerous when abused, as they can cause respiratory depression, an overdose, and even death. People who are prescribed opioids should be monitored closely for any signs of misuse or abuse, and doctors should be aware of the risks associated with prescribing opioids.
Illicit Opioids and Addiction
Illicit opioids are drugs that are not prescribed by a doctor, and they can be even more dangerous than prescription opioids. Illicit opioids include heroin, fentanyl, and other synthetic opioids, and they are often much stronger than prescription opioids. Illicit opioids can be highly addictive, and they can lead to severe health complications and even death.
Illicit opioids have become increasingly available in the US in recent years, and they are often cheaper and more accessible than prescription opioids. This has led to an increase in the number of people addicted to illicit opioids, and it is estimated that over one million people in the US are addicted to illicit opioids.
Treatment and Prevention of Opioid Addiction
Treatment for opioid addiction is available, and there are several options available to those seeking help. Medication-assisted treatment (MAT) is one of the most effective forms of treatment, and it involves the use of medications, such as buprenorphine, to help reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms. Behavioral therapies, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), are also often used to help individuals cope with their addiction.
In addition to treatment, prevention is key to reducing the number of people addicted to opioids. Prevention efforts should focus on educating people about the risks of opioid use and providing access to treatments for those who are already addicted.
Conclusion
Opioid addiction is a serious public health concern in the US, and it is estimated that over 10 million people are addicted to opioids. While prescription opioids are one of the leading contributors to the opioid epidemic, illicit opioids are also a major problem. Treatment and prevention are key to reducing the number of people addicted to opioids, and it is important to provide access to treatment and education to those who need it.
Top 6 Frequently Asked Questions
What Is an Opioid?
An opioid is a type of drug which is derived from the poppy plant and works by binding to opioid receptors in the body. It is used to treat pain and has been abused for its euphoric effect. Opioids can be naturally occurring, synthetic, or semi-synthetic. Common opioids include heroin, oxycodone, hydrocodone, fentanyl, and morphine.
What Is Opioid Addiction?
Opioid addiction is a chronic disease characterized by compulsive drug seeking and use of opioids despite negative consequences. This can include physical and psychological dependence on opioids, leading to difficultly controlling use and cravings. Opioid addiction can be difficult to overcome without the help of medical professionals.
How Many People Are Addicted to Opioids?
It is estimated that in the United States alone, over 2 million people are addicted to opioids. Other estimates suggest that up to 11 million people are misusing opioids. The opioid crisis continues to cause a tremendous public health emergency, with more than 130 people dying every day due to opioid overdose.
What Are the Effects of Opioid Addiction?
The long-term effects of opioid addiction can be serious and life-threatening. These include physical dependence, increased tolerance to the drug, increased risk of overdose, and a variety of psychological and social side effects, such as depression, anxiety, and difficulty in relationships.
Are There Any Treatments for Opioid Addiction?
Yes, there are a variety of treatments for opioid addiction, such as medication-assisted treatment, detoxification, and counseling or therapy. Treatment plans should be tailored to the individual, as each person’s needs and circumstances are different.
What Can I Do to Help Someone with an Opioid Addiction?
If you know someone with an opioid addiction, the best thing you can do is to encourage them to seek help. Offer your support and understanding, and help them access resources such as professional treatment, support groups, or mental health services. You can also help by educating yourself and others about opioid addiction and the dangers of drug misuse.
Descent into opioid addiction captured on video
There is no denying the fact that opioid addiction is a major issue in today’s society. The numbers are staggering and the consequences are far-reaching. While there is no single solution to this problem, it is clear that greater awareness and education, increased access to treatment and support services, and better regulation of prescription opioids will be necessary in order to reduce the number of people affected by opioid addiction. Education and understanding are the first steps in tackling this epidemic.
Francisco Church is a rehabilitation specialist and the chief editor of Recovery Ranger. He creates this site to offer guidance and support to individuals seeking to overcome addiction and achieve lasting sobriety. With extensive experience in the field of addiction treatment, Francisco is dedicated to helping individuals access the resources they need for successful recovery.
- Latest Posts by Francisco Church
-
Is Diethylpropion A Stimulant?
- -
Is Alcohol A Inflammatory?
- -
Does Alcohol Make A Uti Worse?
- All Posts