Francisco Church is a rehabilitation specialist and the chief editor of Recovery Ranger. He creates this site to offer guidance and support to individuals seeking...Read more
Smoking is a habit that many people find hard to break. But how long does it actually take to become addicted to nicotine? This article will explore the answer to this question, as well as the long-term effects of nicotine addiction. We will also look at how to break the cycle of nicotine addiction and offer tips for those looking to quit smoking.
It can take as little as just a few days for someone to become addicted to nicotine. Nicotine is a highly addictive substance found in cigarettes and other tobacco products. It can act quickly on the brain to produce a feeling of pleasure, but it can also lead to addiction. The length of time it takes to become addicted to nicotine can depend on how much and how often someone is exposed to it.
Contents
- How Long Does it Take to Become Addicted to Nicotine?
- What Are The Long-Term Effects of Nicotine Addiction?
- Few Frequently Asked Questions
- What is Nicotine Addiction?
- How Long Does it Take to Get Addicted to Nicotine?
- What are the Symptoms of Nicotine Addiction?
- How Can Nicotine Addiction Be Treated?
- What are the Long-Term Effects of Nicotine Addiction?
- What are the Benefits of Quitting Nicotine?
- How do you know if you’re addicted to Nicotine
- Is Diethylpropion A Stimulant?
- Is Alcohol A Inflammatory?
- Does Alcohol Make A Uti Worse?
How Long Does it Take to Become Addicted to Nicotine?
Nicotine is the addictive stimulant found in cigarettes, cigars and other tobacco products. It is a highly addictive substance, with many people becoming addicted to it after only a few uses. So, how long does it take to become addicted to nicotine? The answer depends on a number of factors, including the individual’s biology, age and the amount of nicotine they are exposed to.
Nicotine acts on the brain quickly and is highly addictive. When someone smokes a cigarette, they can become addicted within a few weeks or even days. This is because nicotine is a powerful stimulant that triggers the release of the “feel-good” chemical dopamine in the brain. The more cigarettes smoked, the more dopamine is released and the stronger the addiction becomes.
Studies have also shown that genetics play a role in how quickly someone becomes addicted to nicotine. People who are genetically predisposed to addiction are more likely to become addicted to nicotine faster than others. In addition, younger people tend to become addicted more quickly than older people, as their brains are still developing and are more susceptible to the effects of nicotine.
How Does Nicotine Addiction Develop?
Nicotine addiction develops over time as the brain becomes increasingly tolerant to its effects. As the person smokes more cigarettes, their brain adjusts to the nicotine levels in the body and begins to crave more of the substance in order to achieve the same level of stimulation. This can lead to physical dependence as the body becomes used to the nicotine and withdrawal symptoms can occur when it is not present.
In addition, nicotine addiction can lead to psychological dependence as the person develops a psychological need for the nicotine in order to feel normal. This can lead to cravings or the urge to smoke even when the person knows it is not good for their health.
What Are The Signs of Nicotine Addiction?
The signs of nicotine addiction can vary from person to person, but there are some common signs that can indicate an addiction. These include: smoking more than usual, increased tolerance to the effects of nicotine, difficulty quitting, cravings for cigarettes and withdrawal symptoms when the person does not smoke.
If you think you may be addicted to nicotine, it is important to talk to your doctor about the best way to quit. Quitting smoking is one of the best ways to reduce your risk of developing serious health problems, such as heart disease and cancer.
What Are The Long-Term Effects of Nicotine Addiction?
Nicotine addiction can have serious long-term effects on the body and mind. Long-term use of nicotine can increase the risk of developing a number of serious health conditions, such as heart disease, stroke, cancer, and lung and respiratory problems. In addition, nicotine addiction can lead to psychological issues, such as anxiety and depression.
Nicotine addiction can also lead to financial problems as the person spends more money on cigarettes and other tobacco products. Quitting smoking can help to reduce the risk of developing these health problems and can also save money in the long run.
How Can Nicotine Addiction Be Treated?
There are a number of treatments available for nicotine addiction, including medications, therapy and lifestyle changes. Medications such as nicotine patches and gum can help to reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms. Therapy can also help to address the psychological aspects of addiction and can help the person to develop healthier coping skills.
Lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking and avoiding triggers, can also help to reduce the risk of relapse and can help the person to stay on track with their treatment plan. Quitting smoking is one of the best ways to reduce the long-term effects of nicotine addiction.
Conclusion
Nicotine addiction can develop quickly, with many people becoming addicted within a few weeks or even days. Genetics, age and the amount of nicotine exposure can all play a role in how quickly someone becomes addicted to nicotine. Nicotine addiction can have serious long-term health and financial consequences, so it is important to talk to your doctor about the best way to quit. There are a number of treatments available for nicotine addiction, including medications, therapy and lifestyle changes. Quitting smoking is one of the best ways to reduce the long-term effects of nicotine addiction.
Few Frequently Asked Questions
What is Nicotine Addiction?
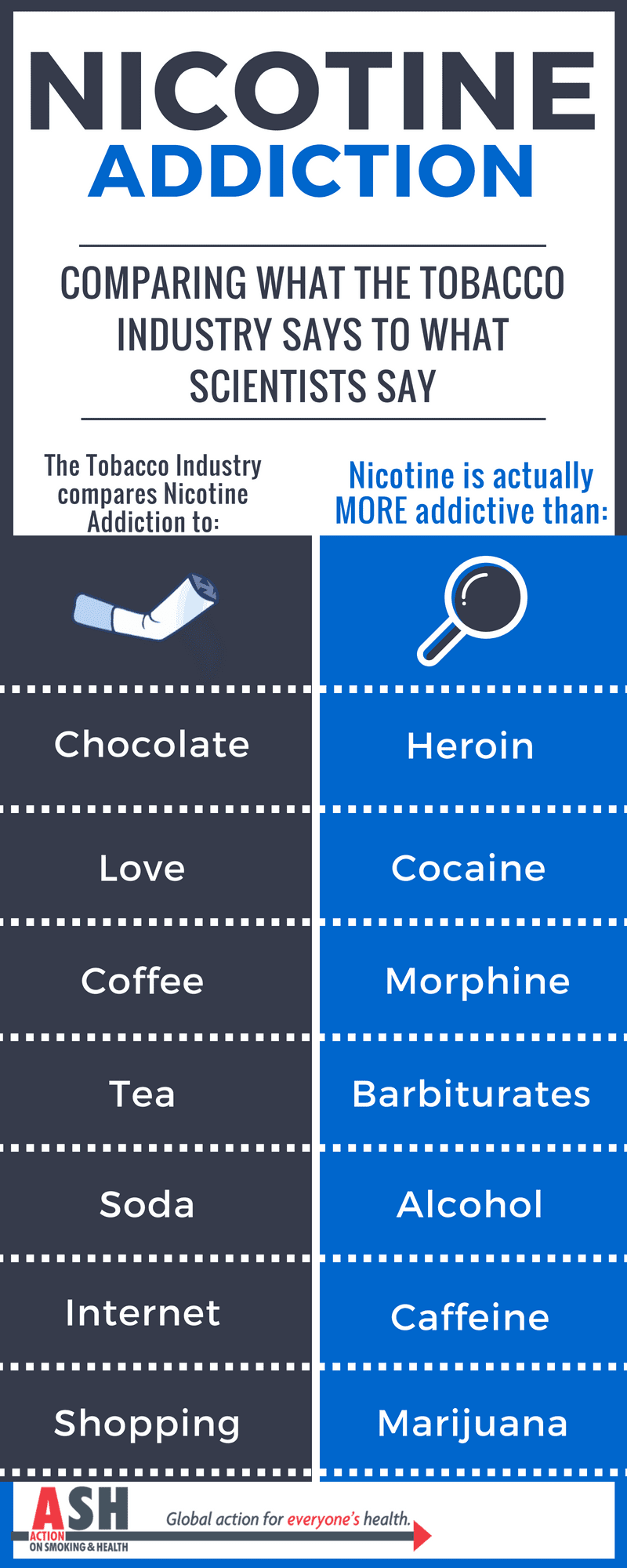
Nicotine addiction is a psychological and physical dependence on nicotine, a chemical found in cigarettes, cigars, pipes, and other tobacco products. People become addicted to nicotine due to its pleasurable effects, which are short-lived, and can lead to an increased tolerance to the substance, meaning that more and more nicotine is required to achieve the same effect. Nicotine addiction can cause serious health problems including cancer and heart disease.
How Long Does it Take to Get Addicted to Nicotine?
It can take as little as a few days or as long as several months to become addicted to nicotine. Factors that contribute to nicotine addiction include the amount of nicotine in the product, how often the person uses it, their body chemistry, and their genetic make-up. People who smoke cigarettes are more likely to become addicted to nicotine more quickly than those who don’t, due to the higher levels of nicotine in cigarettes.
What are the Symptoms of Nicotine Addiction?
The symptoms of nicotine addiction include cravings for nicotine, irritability and restlessness when deprived of nicotine, difficulty concentrating, and an increase in tolerance to nicotine, meaning that more nicotine is needed to achieve the same pleasurable effects. People with nicotine addiction may also experience physical symptoms, such as increased heart rate, increased blood pressure, and increased breathing rate.
How Can Nicotine Addiction Be Treated?
Nicotine addiction can be treated with a combination of medications and behavioral therapy. Nicotine replacement therapy (NRT) is a type of medication that uses nicotine in lower doses to help reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms. Behavioral therapy can help people address underlying issues, such as depression or stress, that contribute to nicotine addiction. Additionally, joining a support group can help people stay motivated and learn from the experiences of others.
What are the Long-Term Effects of Nicotine Addiction?
The long-term effects of nicotine addiction can include an increased risk of cancer and other serious health problems. Nicotine addiction can also lead to an increased risk of stroke, heart disease, and other cardiovascular problems. Additionally, nicotine addiction can cause lung damage, increased risk of respiratory illnesses, and can affect fertility in both men and women.
What are the Benefits of Quitting Nicotine?
The benefits of quitting nicotine are numerous. Within 20 minutes of quitting, blood pressure and heart rate drop, and within a week, circulation and lung function improve. After a few months, cilia – tiny hair-like structures in the lungs – regain normal function, and after a year, the risk of heart attack is cut in half. Quitting nicotine also reduces the risk of cancer and other serious health problems, and helps people save money.
How do you know if you’re addicted to Nicotine
In conclusion, it is clear that nicotine addiction can occur relatively quickly, with some studies showing that it can take as little as 3 weeks of regular use to become addicted to nicotine. Although it is highly recommended to avoid nicotine altogether, it is important to be aware of the risks associated with nicotine use and the potential for addiction.
Francisco Church is a rehabilitation specialist and the chief editor of Recovery Ranger. He creates this site to offer guidance and support to individuals seeking to overcome addiction and achieve lasting sobriety. With extensive experience in the field of addiction treatment, Francisco is dedicated to helping individuals access the resources they need for successful recovery.
- Latest Posts by Francisco Church
-
Is Diethylpropion A Stimulant?
- -
Is Alcohol A Inflammatory?
- -
Does Alcohol Make A Uti Worse?
- All Posts