Francisco Church is a rehabilitation specialist and the chief editor of Recovery Ranger. He creates this site to offer guidance and support to individuals seeking...Read more
Benzodiazepines are commonly prescribed medications used to treat anxiety, insomnia, seizures, and other conditions. But, how long do these medications stay in our systems? This article will provide an overview of the duration of benzodiazepines in the human body and the factors that can affect the length of time they remain in the system. We’ll also look at the implications of having benzodiazepines in your system, including the potential for dependence and the risks associated with long-term use.
Benzodiazepines typically stay in a person’s system for 1-4 days, but this can vary depending on the person’s age, metabolism, and the type and dosage of the drug. Long-acting benzodiazepines, such as diazepam, may remain in the system for up to 10 days.
Contents
- How Long Do Benzodiazepines Remain in the Body?
- How to Reduce the Amount of Time Benzodiazepines Stay in the Body
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Question 1: What are Benzodiazepines?
- Question 2: How Long Do Benzodiazepines Stay in System?
- Question 3: What Factors Affect How Long Benzodiazepines Stay in the System?
- Question 4: Are There Tests to Detect Benzodiazepines in the System?
- Question 5: What Are the Symptoms of Benzodiazepine Withdrawal?
- Question 6: How Can Benzodiazepine Withdrawal Be Managed?
- Is Diethylpropion A Stimulant?
- Is Alcohol A Inflammatory?
- Does Alcohol Make A Uti Worse?
How Long Do Benzodiazepines Remain in the Body?
Benzodiazepines are a class of medications commonly used to treat anxiety and insomnia. They are typically prescribed for short-term use and can be habit-forming if used for a long period. When taken, benzodiazepines enter the body and begin to take effect quickly. The length of time they remain in the body varies based on several factors, including the type of benzodiazepine taken, the dosage, and individual characteristics such as weight, age, and metabolism.
Factors that Affect How Long Benzodiazepines Stay in the Body
The type of benzodiazepine taken is one of the major factors that affects how long the drug remains in the body. Short-acting benzodiazepines, such as alprazolam, are typically metabolized and eliminated from the body much quicker than long-acting benzodiazepines, such as diazepam. The dosage of the benzodiazepine also affects how long it remains in the body. Higher dosages typically take longer to metabolize and be eliminated from the body. Additionally, individual characteristics can affect how long benzodiazepines remain in the body. Factors such as age, weight, and metabolism can all influence how quickly the body can metabolize and eliminate the drug.
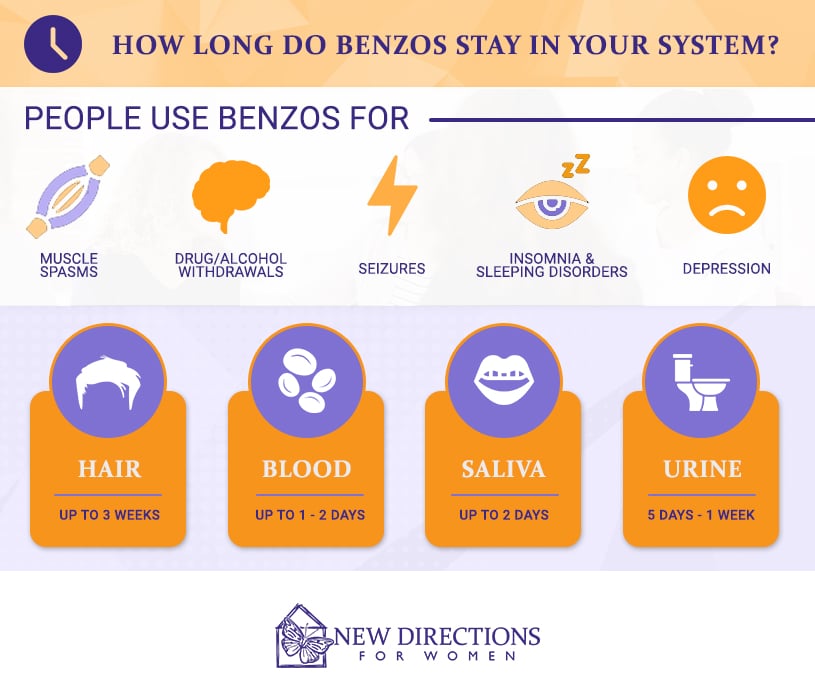
Benzodiazepines in Urine, Blood, and Saliva
Benzodiazepines can be detected in urine, blood, and saliva tests. In urine tests, benzodiazepines can usually be detected within 12-48 hours of taking the last dose. In blood tests, benzodiazepines can usually be detected within 12-24 hours of taking the last dose. In saliva tests, benzodiazepines can usually be detected within 12-48 hours of taking the last dose.
Benzodiazepines in Hair
Benzodiazepines can also be detected in hair tests. Hair tests are typically the most accurate test for detecting benzodiazepines, as they can detect the drugs for much longer periods of time than urine, blood, or saliva tests. In hair tests, benzodiazepines can typically be detected for up to 90 days after taking the last dose.
How to Reduce the Amount of Time Benzodiazepines Stay in the Body
The most effective way to reduce the amount of time benzodiazepines remain in the body is to take the lowest possible dose for the shortest amount of time. Additionally, it is important to take the medication exactly as prescribed by a doctor and to never take more than the recommended dose. Additionally, it may be beneficial to drink plenty of fluids and exercise regularly, as this can help speed up the metabolism and help the body eliminate the drug more quickly.
Importance of Talking to a Doctor
It is important to talk to a doctor before taking benzodiazepines and to take the medication exactly as prescribed. It is also important to talk to a doctor if any side effects occur while taking the medication, as the dosage may need to be adjusted. If a person has been taking benzodiazepines for a long period of time, it is important to talk to a doctor before stopping the medication, as the body may need to be gradually weaned off the medication.
Risks of Misusing Benzodiazepines
It is important to take benzodiazepines only as prescribed by a doctor, as there are risks associated with misusing the medication. Misusing benzodiazepines can increase the risk of dependence and addiction and can also increase the risk of side effects, such as drowsiness, confusion, and difficulty breathing. Additionally, taking benzodiazepines with other medications or alcohol can increase the risk of dangerous side effects and even death.
Frequently Asked Questions
Question 1: What are Benzodiazepines?
Answer: Benzodiazepines are a class of drugs commonly prescribed to treat anxiety, insomnia, and seizures. They work by increasing the activity of a neurotransmitter in the brain called gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), which is thought to reduce the activity of nerve cells in the brain and produce a calming effect. Benzodiazepines are also known as “benzos” and are available in both short- and long-acting forms. Examples of benzodiazepines include alprazolam (Xanax), clonazepam (Klonopin), and diazepam (Valium).
Question 2: How Long Do Benzodiazepines Stay in System?
Answer: The amount of time benzodiazepines stay in the system depends on several factors, including the type of benzodiazepine taken, its dosage, the individual’s metabolism, and how often the drug is taken. Generally, benzodiazepines will remain in the system for two to four days. However, some benzodiazepines can remain in the system for up to two weeks.
Question 3: What Factors Affect How Long Benzodiazepines Stay in the System?
Answer: There are several factors that can affect how long benzodiazepines stay in the system. These factors include the type of benzodiazepine taken, its dosage, the individual’s metabolism, and how often the drug is taken. For instance, a higher dose or more frequent use of a benzodiazepine can extend the amount of time that the drug remains in the system. Additionally, some individuals may have a faster metabolism than others, which can also affect how quickly the drug is metabolized and eliminated from the system.
Question 4: Are There Tests to Detect Benzodiazepines in the System?
Answer: Yes, there are tests available to detect benzodiazepines in the system. These tests are typically done using a urine or blood sample. Urine tests are the most common type of test used to detect benzodiazepines. Typically, the test can detect benzodiazepines in the system for up to three days after the last dose was taken. Blood tests can detect benzodiazepines in the system for up to two weeks after the last dose was taken.
Question 5: What Are the Symptoms of Benzodiazepine Withdrawal?
Answer: The symptoms of benzodiazepine withdrawal can vary depending on the type of benzodiazepine taken and the individual’s tolerance. Common symptoms of benzodiazepine withdrawal include anxiety, insomnia, nausea, muscle cramps, headaches, tremors, and seizures. Additionally, more severe symptoms can occur, such as psychosis, confusion, hallucinations, and delirium.
Question 6: How Can Benzodiazepine Withdrawal Be Managed?
Answer: Benzodiazepine withdrawal should be managed under the supervision of a medical professional. Treatment typically involves tapering the dose of the benzodiazepine over time to reduce the risk of severe withdrawal symptoms. Additionally, medications may be prescribed to help manage the withdrawal symptoms and prevent relapse. Psychological support is also important and can help the individual cope with the symptoms of withdrawal and transition into a healthier lifestyle.
To conclude, benzodiazepines can stay in your system for different lengths of time depending on the type of benzodiazepine and individual factors such as age, metabolism, and body size. Generally, benzodiazepines can be detected in urine tests for up to two weeks, in blood tests for up to two days, and in saliva tests for up to three days. It is important to speak to a healthcare professional when taking benzodiazepines to ensure they are used safely and appropriately.
Francisco Church is a rehabilitation specialist and the chief editor of Recovery Ranger. He creates this site to offer guidance and support to individuals seeking to overcome addiction and achieve lasting sobriety. With extensive experience in the field of addiction treatment, Francisco is dedicated to helping individuals access the resources they need for successful recovery.
- Latest Posts by Francisco Church
-
Is Diethylpropion A Stimulant?
- -
Is Alcohol A Inflammatory?
- -
Does Alcohol Make A Uti Worse?
- All Posts