Francisco Church is a rehabilitation specialist and the chief editor of Recovery Ranger. He creates this site to offer guidance and support to individuals seeking...Read more
Alcohol is an incredibly popular recreational beverage, but its impacts on cognitive functioning are often overlooked. Does alcohol cause brain fog, or is it a myth? In this article, we will explore the effects of alcohol on the brain and investigate whether it can indeed lead to brain fog. We will also discuss potential solutions for those who wish to reduce their risk of alcohol-related cognitive decline.
Contents
- Alcohol Consumption and Brain Fog
- Top 6 Frequently Asked Questions
- Does Alcohol Cause Brain Fog?
- What is Brain Fog?
- How Does Alcohol Affect Cognitive Function?
- What Are the Short-Term Effects of Alcohol?
- What are the Long-Term Effects of Alcohol?
- Can Alcohol Consumption Be Managed?
- Brain Fog After Quitting Drinking!
- Is Diethylpropion A Stimulant?
- Is Alcohol A Inflammatory?
- Does Alcohol Make A Uti Worse?
Alcohol Consumption and Brain Fog
Alcohol consumption, especially in excess, is a major risk factor for developing brain fog. Brain fog is a condition marked by a lack of mental clarity and decreased cognitive functioning. Alcohol impairs the brain’s ability to focus and concentrate, leading to confusion and forgetfulness. It also affects the brain’s ability to recall information and process new information. As a result, people who drink heavily often have difficulty with tasks that require quick and accurate thinking.
Alcohol also affects the brain’s ability to regulate mood and emotions. People who drink heavily may become more prone to mood swings, irritability, and depression. These symptoms can further contribute to brain fog and make it more difficult to think clearly. Additionally, alcohol can disrupt the body’s sleep cycle, which can leave people feeling tired and foggy throughout the day.
The Effects of Long-Term Alcohol Consumption
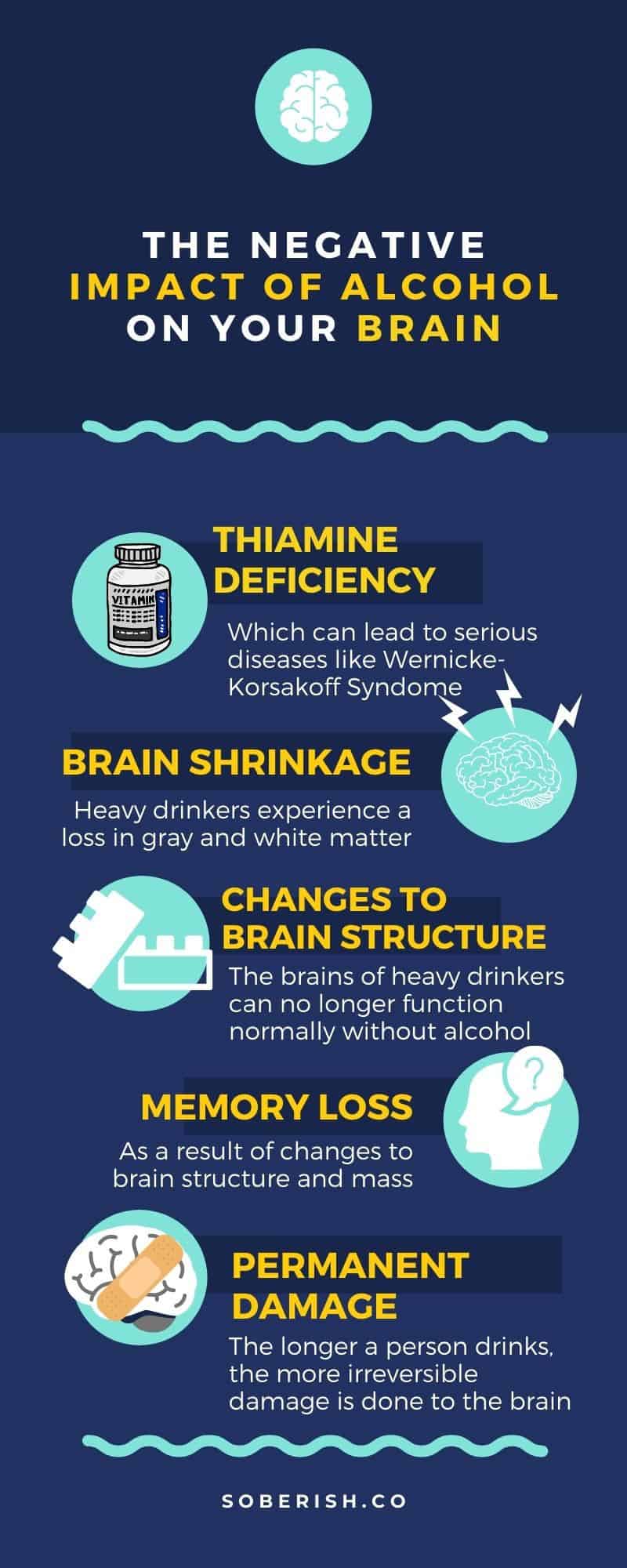
The effects of long-term alcohol consumption can be even more serious. Chronic alcohol consumption can lead to long-term brain damage, which can have a serious impact on a person’s cognitive functioning. Damage to the brain’s frontal lobe, which is responsible for higher-order thinking, can lead to a decrease in cognitive functioning, including memory and concentration.
Chronic alcohol consumption can also lead to vitamin B1 (Thiamine) deficiency, which can further contribute to brain fog. Vitamin B1 is essential for the proper functioning of the brain and nervous system. A lack of vitamin B1 can lead to confusion, memory problems, and difficulty concentrating.
Tips for Minimizing Brain Fog
For people who are dealing with the effects of brain fog due to alcohol consumption, there are a few things they can do to help reduce their symptoms. The first step is to stop drinking alcohol altogether. This will help reduce the amount of damage done to the brain and allow the body to begin to heal.
It is also important to get enough rest and to eat a healthy, balanced diet. Eating foods that are rich in vitamins and minerals, such as fruits and vegetables, can help support the brain and improve cognitive functioning. Additionally, engaging in regular physical activity can help increase blood flow to the brain and improve alertness and concentration.
Seeking Professional Help
If brain fog due to alcohol consumption persists or worsens, it is important to seek help from a medical professional. A doctor can assess the individual’s symptoms and recommend a treatment plan that is tailored to their specific needs. Treatment may include medications to help with mood stabilization, cognitive therapy to help improve mental functioning, and nutritional counseling to ensure the individual is getting enough vitamins and nutrients.
The Impact of Alcohol on Mental Health
Alcohol can have a significant impact on mental health. In addition to brain fog, it can lead to anxiety, depression, and other mental health disorders. It is important to be mindful of how much alcohol is consumed and to seek help if there are concerns about its effects on mental health.
Top 6 Frequently Asked Questions
Does Alcohol Cause Brain Fog?
Answer: Yes, alcohol can cause brain fog. The short-term effects of alcohol can impair your concentration and make it difficult to think clearly. In the long-term, excessive alcohol consumption can lead to permanent brain damage and cognitive decline.
What is Brain Fog?
Answer: Brain fog is a term used to describe feelings of confusion, difficulty concentrating, and forgetfulness. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including stress, lack of sleep, and poor nutrition. In some cases, it can also be caused by excessive alcohol consumption.
How Does Alcohol Affect Cognitive Function?
Answer: When consumed in excess, alcohol can have a negative impact on cognitive function. Alcohol impairs your ability to think clearly, affects your memory, and can lead to slower reaction times. In addition, long-term alcohol abuse can lead to permanent brain damage and cognitive decline.
What Are the Short-Term Effects of Alcohol?
Answer: The short-term effects of alcohol include impaired judgment, slowed reflexes, and difficulty concentrating. In addition, alcohol can cause blurred vision, slurred speech, and impaired motor coordination.
What are the Long-Term Effects of Alcohol?
Answer: Long-term alcohol abuse can lead to permanent brain damage and cognitive decline. It can also increase the risk of certain diseases, such as stroke and liver disease. In addition, heavy alcohol consumption can lead to mental health issues, such as depression and anxiety.
Can Alcohol Consumption Be Managed?
Answer: Yes, alcohol consumption can be managed. It is important to practice moderation and to limit your alcohol consumption to the recommended guidelines. It is also important to be aware of the potential risks of excessive alcohol consumption and to seek help if necessary.
Brain Fog After Quitting Drinking!
In conclusion, the research shows that alcohol can cause brain fog. It can lead to short-term memory problems, difficulty concentrating, and slower reaction times. Although these effects are usually temporary, long-term alcohol use can cause more serious cognitive impairments. Therefore, it is best to drink in moderation and to consult with a physician or other healthcare professional if you experience any of these symptoms.
Francisco Church is a rehabilitation specialist and the chief editor of Recovery Ranger. He creates this site to offer guidance and support to individuals seeking to overcome addiction and achieve lasting sobriety. With extensive experience in the field of addiction treatment, Francisco is dedicated to helping individuals access the resources they need for successful recovery.
- Latest Posts by Francisco Church
-
Is Diethylpropion A Stimulant?
- -
Is Alcohol A Inflammatory?
- -
Does Alcohol Make A Uti Worse?
- All Posts