Francisco Church is a rehabilitation specialist and the chief editor of Recovery Ranger. He creates this site to offer guidance and support to individuals seeking...Read more
Opiates are powerful drugs that are commonly prescribed to treat pain, but how do they affect the body’s serotonin levels? Serotonin is an essential neurotransmitter that regulates mood, memory, sleep, and other bodily functions. In this article, we will explore the effects of opiate use on serotonin production, including the potential for opiate addiction and withdrawal symptoms. We will also discuss the potential for serotonin-targeted treatments to help reduce the risk of opiate misuse.
Contents
- Do Opiates Affect Serotonin?
- What is Serotonin?
- How Do Opiates Affect Serotonin?
- Short and Long-Term Effects
- Treatment Options
- Risks of Using Opiates
- Frequently Asked Questions
- What are Opiates?
- How Do Opiates Affect Serotonin?
- What are the Risks Associated with Taking Opiates?
- What is Serotonin Syndrome?
- Can Opiates be Used to Treat Serotonin Syndrome?
- What are the Alternatives to Opiates for Pain Management?
- This Is What Happens to Your Brain on Opioids | Short Film Showcase
- Is Diethylpropion A Stimulant?
- Is Alcohol A Inflammatory?
- Does Alcohol Make A Uti Worse?
Do Opiates Affect Serotonin?
What is Serotonin?
Serotonin is a neurotransmitter that is naturally produced by the body and plays an important role in cognitive and emotional functions. It is found in the brain, gastrointestinal tract, and other areas of the body. Serotonin helps regulate mood, sleep, appetite, and other important functions. Low serotonin levels have been linked to depression, anxiety, and other mental health conditions.
Serotonin is produced from the essential amino acid tryptophan and is released by nerve cells in the brain. It is then taken up by other nerve cells and acts as a neurotransmitter to regulate many bodily functions. Serotonin is also involved in the regulation of pain, appetite, memory, and learning.
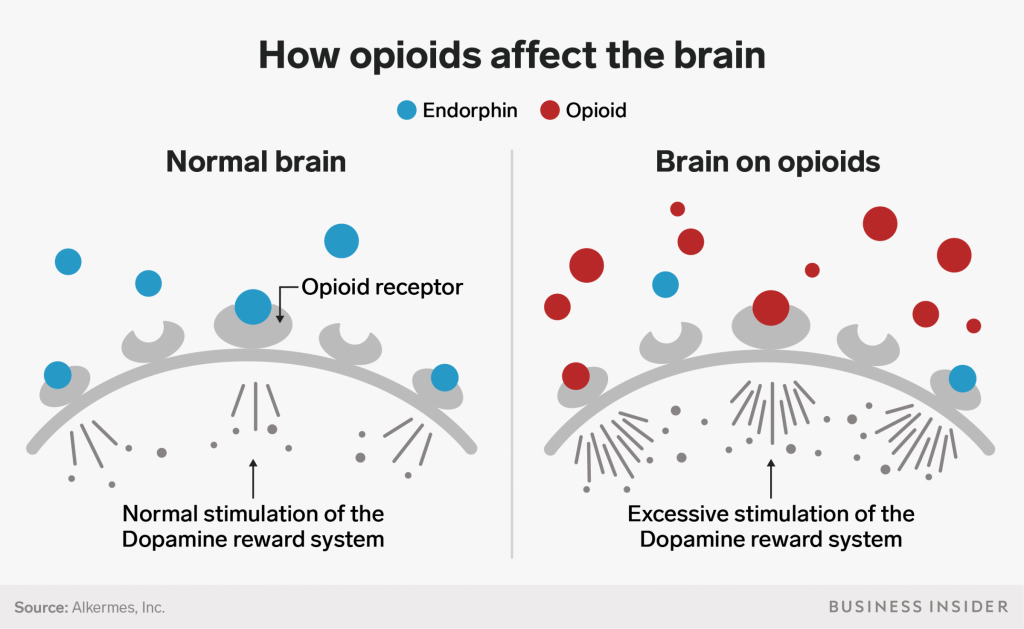
How Do Opiates Affect Serotonin?
Opiate drugs, such as heroin, morphine, and codeine, are derived from the opium poppy plant and act on specific opioid receptors in the brain. Opiates interact with various neurotransmitters, including serotonin.
When opiates are taken, they can increase the amount of serotonin in the brain. This can lead to feelings of euphoria, pleasure, and relaxation. Opiates can also decrease the amount of serotonin in the brain, leading to feelings of depression and anxiety.
In addition, opiates can interfere with the way serotonin is produced, transported, and metabolized, leading to a decrease in serotonin levels in the long term. This can lead to an imbalance in serotonin, which can cause a variety of mental health issues, such as depression and anxiety.
Short and Long-Term Effects
The effects of opiates on serotonin levels are both short-term and long-term. In the short-term, opiates can lead to increased feelings of pleasure and relaxation, as well as decreased feelings of depression and anxiety.
In the long-term, opiates can lead to a decrease in serotonin levels, which can lead to an imbalance in serotonin and an increased risk of mental health issues. In addition, long-term use of opiates can lead to addiction, tolerance, and other physical and psychological issues.
Treatment Options
If you are struggling with opiate addiction, it is important to seek treatment as soon as possible. There are a variety of treatment options available, such as medication-assisted therapy and counseling.
Medication-assisted therapy involves the use of medications, such as buprenorphine, to help reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms. Counseling can help address the underlying issues that led to the addiction and provide support and guidance throughout the recovery process.
Risks of Using Opiates
Using opiates can lead to a variety of physical and psychological issues, such as addiction, tolerance, and decreased serotonin levels. It is important to be aware of the risks associated with opiate use and to seek help if you are struggling with addiction.
Addiction
Using opiates can lead to physical dependence and addiction. Physical dependence occurs when the body becomes used to the drug and needs it in order to function normally. Addiction occurs when the user becomes psychologically dependent on the drug and begins to crave it despite the negative consequences.
Tolerance
Tolerance occurs when the body becomes used to the drug and needs more of it in order to achieve the desired effect. This can lead to an increased risk of overdose and other adverse effects.
Decreased Serotonin Levels
Long-term use of opiates can lead to a decrease in serotonin levels, which can lead to an imbalance in serotonin and an increased risk of mental health issues, such as depression and anxiety.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are Opiates?
Opiates are drugs derived from the opium poppy plant. They are used to treat pain, as well as to produce feelings of euphoria and relaxation. Common opiate drugs include morphine, codeine, oxycodone, and heroin.
How Do Opiates Affect Serotonin?
Opiates affect serotonin in the brain by binding to opioid receptors, which causes an increase in the release of serotonin. This increased serotonin can cause feelings of pleasure, but can also lead to serotonin syndrome, a serious and potentially deadly condition caused by too much serotonin in the body.
What are the Risks Associated with Taking Opiates?
Taking opiates can be risky because of their addictive potential and potential for overdose. Opiates can also interact with other medications, and can cause serious side effects such as constipation, nausea, and respiratory depression.
What is Serotonin Syndrome?
Serotonin syndrome is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition caused by an excess of serotonin in the body. Symptoms of serotonin syndrome include confusion, agitation, increased heart rate, sweating, and hallucinations.
Can Opiates be Used to Treat Serotonin Syndrome?
No, opiates should not be used to treat serotonin syndrome. Opiates can actually make the condition worse by further increasing serotonin levels in the body. Instead, serotonin syndrome should be treated with medications that reduce serotonin levels, such as benzodiazepines or cyproheptadine.
What are the Alternatives to Opiates for Pain Management?
There are many alternatives to opiates for pain management, including non-opioid medications such as ibuprofen and acetaminophen, as well as non-pharmacological treatments such as physical therapy, acupuncture, and massage. Additionally, there are other opioid medications that are less addictive than opiates, such as buprenorphine and naloxone.
This Is What Happens to Your Brain on Opioids | Short Film Showcase
In conclusion, opiates have a profound effect on serotonin levels in the brain and can lead to a variety of physical and mental health problems. As such, it is important to be aware of the potential risks associated with taking opiates and seek medical advice if you are at risk of developing a serotonin-related disorder. With proper guidance and care, the effects of opiates on serotonin levels can be managed and minimized, allowing people to benefit from the drug without putting their health at risk.
Francisco Church is a rehabilitation specialist and the chief editor of Recovery Ranger. He creates this site to offer guidance and support to individuals seeking to overcome addiction and achieve lasting sobriety. With extensive experience in the field of addiction treatment, Francisco is dedicated to helping individuals access the resources they need for successful recovery.
- Latest Posts by Francisco Church
-
Is Diethylpropion A Stimulant?
- -
Is Alcohol A Inflammatory?
- -
Does Alcohol Make A Uti Worse?
- All Posts