Francisco Church is a rehabilitation specialist and the chief editor of Recovery Ranger. He creates this site to offer guidance and support to individuals seeking...Read more
Anxiety is a debilitating mental health condition that affects millions of people around the world. While there are many potential causes of anxiety, one that is often overlooked is opiate use. Opiates, such as heroin and prescription painkillers, can have a powerful effect on the brain and can cause a range of physical and psychological symptoms, including anxiety. In this article, we will explore how opiates can cause anxiety and how to manage the condition.
Yes, opiates can cause anxiety. This is because opiates can cause a number of changes in the brain, including increased levels of dopamine and serotonin, which can lead to feelings of anxiety or panic attacks. Other symptoms can include difficulty concentrating, irritability, restlessness, rapid heart rate, and difficulty sleeping. People taking opiates can experience both physical and psychological dependence, which can worsen symptoms of anxiety. It is important to talk to your doctor if you are taking opiates and experiencing anxiety.
Contents
- Can Opiate Use Lead to Anxiety?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- What are opiates?
- Can opiates cause anxiety?
- How long can anxiety last after taking opiates?
- What are the signs and symptoms of anxiety caused by opiates?
- What are the treatment options for anxiety caused by opiates?
- Can anxiety caused by opiates be prevented?
- This Is What Happens to Your Brain on Opioids | Short Film Showcase
- Is Diethylpropion A Stimulant?
- Is Alcohol A Inflammatory?
- Does Alcohol Make A Uti Worse?
Can Opiate Use Lead to Anxiety?
Opiate use can affect people in many ways, and one of these is an increased risk of developing anxiety. Opiates are a type of drug that binds to the body’s opioid receptors, calming the user and providing a sense of euphoria. While they are often prescribed to treat pain, they can also be abused, leading to a host of negative side effects, including anxiety.
When someone takes opiates, the drug binds to opioid receptors in the brain, creating a sense of relaxation and euphoria. However, this feeling is short-lived, and when the effects wear off, the user may experience withdrawal symptoms, including anxiety. This is due to the sudden decrease in the body’s opioid levels, which can cause a feeling of uneasiness and worry.
In addition to withdrawal symptoms, long-term opiate use can also cause anxiety. This is because the body becomes used to the presence of the drug, and when it’s not present, the user may feel anxious. This is often referred to as “opiate-induced anxiety” and can be very difficult to treat.
How Does Opiate Use Lead to Anxiety?
There are several ways in which opiate use can lead to anxiety. As mentioned above, one of the most common is withdrawal symptoms. When someone stops taking opiates, they may experience a variety of symptoms, including anxiety, restlessness, irritability, and depression. This is because the body has become used to the presence of the drug, and when it’s not present, the user may feel anxious.
Another way in which opiate use can lead to anxiety is by affecting the brain’s reward system. This is because opiates bind to the brain’s opioid receptors, creating a sense of euphoria. Over time, the brain becomes accustomed to this feeling, and when it’s not present, the user may experience a feeling of anxiety.
What Are the Symptoms of Opiate-Induced Anxiety?
The symptoms of opiate-induced anxiety can vary from person to person, but some of the most common include:
• Difficulty concentrating
• Racing thoughts
• Muscle tension
• Difficulty sleeping
• Panic attacks
• Feelings of restlessness
If someone is experiencing any of these symptoms, they should seek help from a medical professional.
How Is Opiate-Induced Anxiety Treated?
The treatment for opiate-induced anxiety will depend on the individual, but some of the most common treatments include:
Psychotherapy
Psychotherapy, or “talk therapy”, can help a person understand their anxiety and learn new coping skills. This can include cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), which can help a person identify and challenge negative thoughts that may be contributing to their anxiety.
Medication
In some cases, medication may be prescribed to help reduce anxiety symptoms. This can include antidepressants, anti-anxiety medications, or other medications that can help balance the body’s chemistry.
Alternative Treatments
In addition to psychotherapy and medication, alternative treatments such as yoga, meditation, and acupuncture can also help reduce anxiety symptoms. These treatments can help a person relax and find their inner balance.
What Are the Long-Term Effects of Opiate Use?
Opiate use can lead to a variety of long-term effects, including addiction, physical dependence, and even death. In addition, long-term use can cause cognitive impairments, as well as an increased risk of developing mental health disorders such as depression and anxiety.
Conclusion
Opiate use can lead to an increased risk of developing anxiety, both through withdrawal symptoms and through long-term use. It is important to seek professional help if you are experiencing any of the symptoms of opiate-induced anxiety, as the long-term effects of opiate use can be severe.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are opiates?
Opiates are a type of drug that are derived from the poppy plant. They are used to relieve pain and can have a calming effect on the body. Opiates are also known as narcotics and include drugs such as morphine, codeine, oxycodone, and hydrocodone.
Can opiates cause anxiety?
Yes, opiates can cause anxiety. Opiates can have a calming effect on the body, but in some cases, they can also have the opposite effect and cause feelings of anxiety and panic. This is because opiates can affect the body’s natural balance of chemicals and hormones, leading to feelings of anxiety and fear.
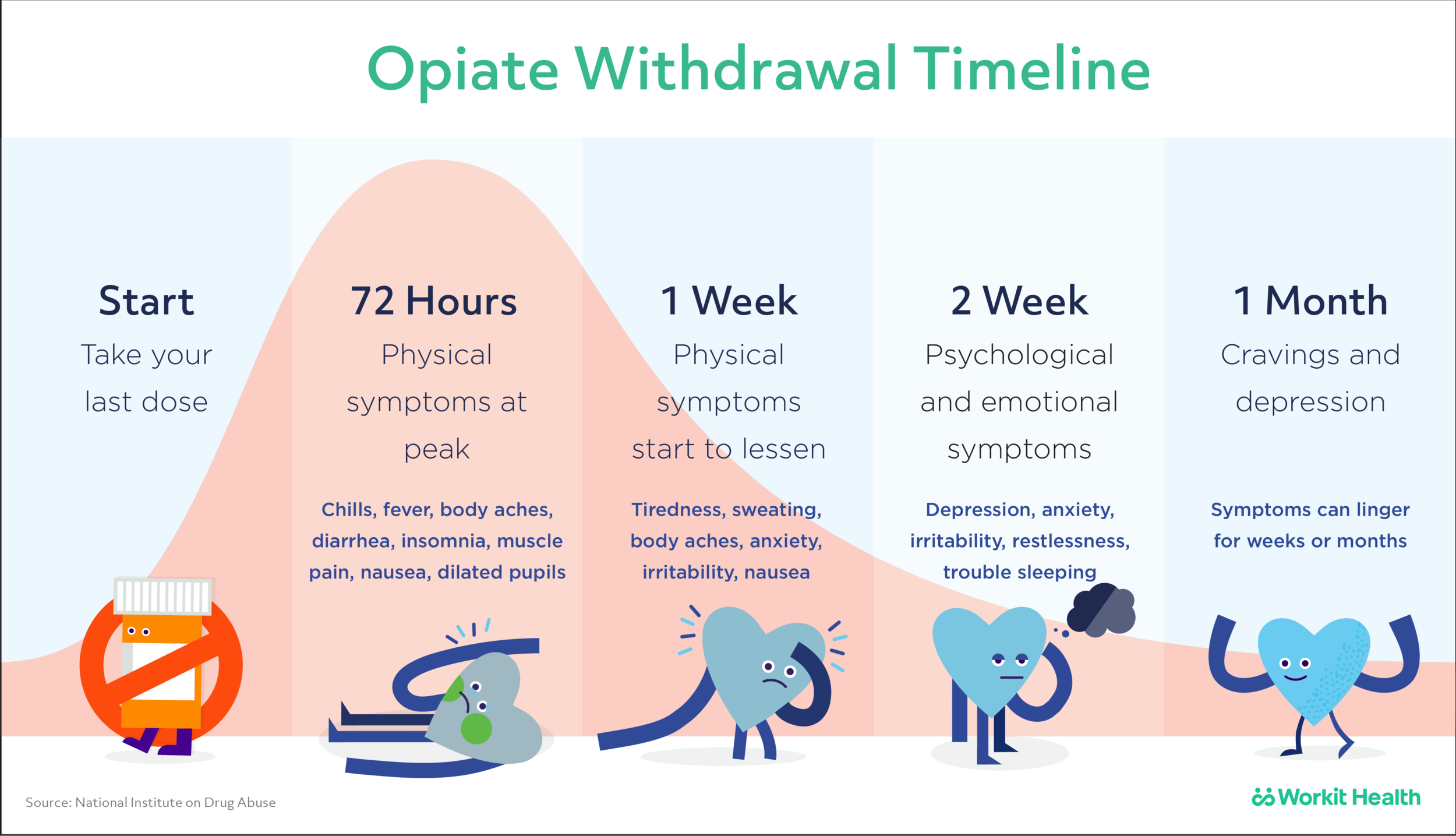
How long can anxiety last after taking opiates?
The duration of anxiety caused by opiates can vary from person to person. Some people may experience anxiety for only a few hours, while others may experience it for days or even weeks. In some cases, the anxiety may not go away until the person has completely stopped taking the opiate.
What are the signs and symptoms of anxiety caused by opiates?
The signs and symptoms of anxiety caused by opiates can include sweating, trembling, difficulty breathing, restlessness, racing thoughts, rapid heartbeat, and feelings of panic or dread.
What are the treatment options for anxiety caused by opiates?
The treatment for anxiety caused by opiates depends on the severity of the symptoms. In some cases, therapy may be recommended to help the person manage their anxiety. Medication, such as anti-anxiety drugs or antidepressants, may also be prescribed to help reduce the symptoms of anxiety.
Can anxiety caused by opiates be prevented?
In some cases, anxiety caused by opiates can be prevented by avoiding or reducing the amount of opiates taken. If a person is taking opiates as prescribed, they should discuss any concerns they have with their doctor. In addition, it is important to manage stress levels and to get plenty of rest and exercise.
This Is What Happens to Your Brain on Opioids | Short Film Showcase
In conclusion, while opiates may help to manage pain, they can also cause anxiety. This is especially true when opiates are taken in high doses, or when a person has a vulnerability to anxiety. It is important for individuals to be aware of the potential for anxiety when taking opiates. If you or someone you know is taking opiates, it is important to talk to a doctor and monitor the person’s mental health. With careful monitoring and medical support, it is possible to manage the effects of opiates and anxiety.
Francisco Church is a rehabilitation specialist and the chief editor of Recovery Ranger. He creates this site to offer guidance and support to individuals seeking to overcome addiction and achieve lasting sobriety. With extensive experience in the field of addiction treatment, Francisco is dedicated to helping individuals access the resources they need for successful recovery.
- Latest Posts by Francisco Church
-
Is Diethylpropion A Stimulant?
- -
Is Alcohol A Inflammatory?
- -
Does Alcohol Make A Uti Worse?
- All Posts