Francisco Church is a rehabilitation specialist and the chief editor of Recovery Ranger. He creates this site to offer guidance and support to individuals seeking...Read more
Psychosis is a condition in which a person’s perception of reality is distorted, and they may experience hallucinations or delusions. While psychosis can be caused by a variety of factors, such as physical illness or psychological trauma, certain drugs can also cause this condition. In this article, we will explore the link between drugs and psychosis, and discuss the potential long-term effects of using drugs and how to prevent them.
Contents
- Can Drugs Cause Psychosis?
- What is Psychosis?
- The Symptoms of Drug-Induced Psychosis
- Frequently Asked Questions
- What is Psychosis?
- What are the Causes of Psychosis?
- Can Drugs Cause Psychosis?
- What are the Symptoms of Drug-induced Psychosis?
- How is Drug-induced Psychosis Treated?
- What Preventative Measures Can Be Taken to Avoid Drug-induced Psychosis?
- Psychosis explained simply [Introduction to Drug-Indcued Psychosis]
- Is Diethylpropion A Stimulant?
- Is Alcohol A Inflammatory?
- Does Alcohol Make A Uti Worse?
Can Drugs Cause Psychosis?
What is Psychosis?
Psychosis is a mental disorder characterized by impaired thinking, emotions, and behaviors. It can include hallucinations, delusions, and disorganized speech and behavior. People with psychosis often experience distress, confusion, and difficulty functioning in daily life. While psychosis can be caused by mental illness, it can also be caused by certain drugs or medications.
Types of Drugs that Can Cause Psychosis
Drugs that can cause psychosis include stimulants, opioids, hallucinogens, and marijuana. Stimulants such as cocaine, amphetamine, and methamphetamine can cause psychotic symptoms such as hallucinations, delusions, and disorganized thoughts and behavior. Opioids such as heroin and prescription painkillers can also cause psychotic symptoms, including paranoia and confusion. Hallucinogens such as LSD and psilocybin mushrooms can also cause psychotic symptoms, as can marijuana if used in large amounts or for a prolonged period of time.
The Risk Factors for Drug-Induced Psychosis
The risk factors for drug-induced psychosis vary depending on the type of drug. For stimulants, the risk of psychosis increases with higher doses, longer duration of use, and a history of mental illness. For opioids, the risk increases with prolonged use and higher doses. For hallucinogens, the risk increases with higher doses, a history of mental illness, and a family history of mental illness. For marijuana, the risk increases with prolonged use and higher doses.
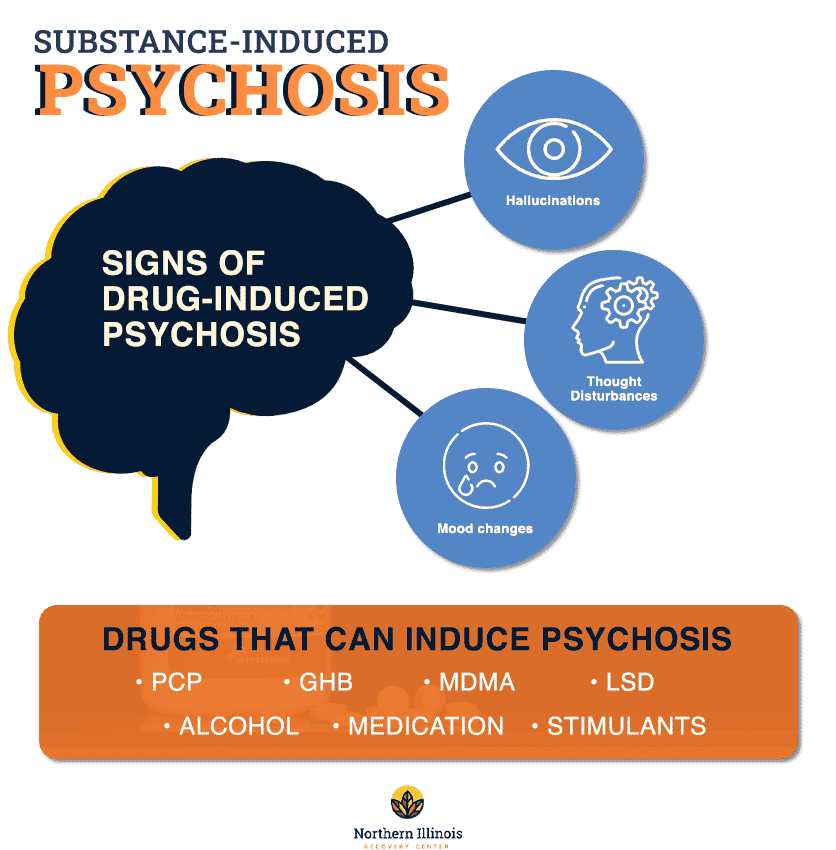
The Symptoms of Drug-Induced Psychosis
The symptoms of drug-induced psychosis vary depending on the type of drug. Stimulants can cause hallucinations, paranoia, delusions, disorganized thoughts and behavior, and agitation. Opioids can cause hallucinations, delusions, confusion, and incoherent speech. Hallucinogens can cause hallucinations, disorganized thoughts, and delusions. Marijuana can cause paranoia, delusions, and disorganized thoughts and behavior.
How is Drug-Induced Psychosis Diagnosed?
Drug-induced psychosis is typically diagnosed by a mental health professional based on a person’s symptoms and history of drug use. The mental health professional may also use laboratory tests to confirm the presence of drugs in the person’s system.
Treatment for Drug-Induced Psychosis
The treatment for drug-induced psychosis typically involves discontinuing the drug and managing the symptoms with medications and psychotherapy. In some cases, hospitalization may be necessary to ensure the person’s safety and provide more intensive treatment. The drug-induced psychosis should resolve once the drug is discontinued and the person is stabilized.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Psychosis?
Psychosis is a mental condition where an individual has difficulty in distinguishing reality from fantasy. It can manifest in many forms, including hallucinations, delusions, paranoia, and disorganized thinking. Symptoms of psychosis can range from mild to severe and can lead to significant disruption in a person’s daily life.
What are the Causes of Psychosis?
Psychosis can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetics, brain chemistry, certain medical conditions, and drug use. In some cases, psychosis can also be triggered by emotional trauma or significant stress. Additionally, certain types of drugs, including hallucinogens, stimulants, and marijuana, can induce a psychotic episode.
Can Drugs Cause Psychosis?
Yes, certain types of drugs can cause psychosis. Hallucinogens, stimulants, and marijuana can all induce a psychotic episode when taken in large doses or in combination with other drugs. Additionally, certain prescription medications, such as antipsychotics, can also cause psychosis when taken in high doses.
What are the Symptoms of Drug-induced Psychosis?
The symptoms of drug-induced psychosis can vary depending on the type of drug used. Common signs of drug-induced psychosis include hallucinations, delusions, disorganized thinking and speech, paranoia, and severe mood swings. Additionally, drug-induced psychosis can lead to violent behavior and suicidal thoughts.
How is Drug-induced Psychosis Treated?
Treatment for drug-induced psychosis typically involves a combination of medication and psychotherapy. Medication can be used to reduce the symptoms of psychosis, while psychotherapy can help an individual understand their triggers and develop healthier coping strategies. Additionally, in some cases, hospitalization may be necessary to ensure the safety of the individual.
What Preventative Measures Can Be Taken to Avoid Drug-induced Psychosis?
The best way to avoid drug-induced psychosis is to abstain from using drugs or limit the use of drugs to recreational use only. Additionally, individuals should be aware of the potential risks associated with taking certain drugs and should consult a doctor before using any substance. It is also important to be mindful of the dosage of any medication prescribed by a doctor, as taking too much can lead to psychosis. Finally, individuals should seek help if they notice any signs of psychosis in themselves or someone they know.
Psychosis explained simply [Introduction to Drug-Indcued Psychosis]
It is clear that certain drugs can cause psychosis or psychotic episodes in people, including those with no pre-existing mental health issues. While some drugs can be very beneficial in treating mental health conditions, it is important to note that they can also have a very serious and detrimental effect on mental health in certain individuals. Therefore, it is essential to speak to a healthcare professional before taking any form of medication, including those prescribed by your doctor, to ensure that you can manage any potential risks before taking them.
Francisco Church is a rehabilitation specialist and the chief editor of Recovery Ranger. He creates this site to offer guidance and support to individuals seeking to overcome addiction and achieve lasting sobriety. With extensive experience in the field of addiction treatment, Francisco is dedicated to helping individuals access the resources they need for successful recovery.
- Latest Posts by Francisco Church
-
Is Diethylpropion A Stimulant?
- -
Is Alcohol A Inflammatory?
- -
Does Alcohol Make A Uti Worse?
- All Posts