Francisco Church is a rehabilitation specialist and the chief editor of Recovery Ranger. He creates this site to offer guidance and support to individuals seeking...Read more
Mental health issues have been a topic of conversation for decades, but only recently have we begun to recognize them for what they are: a disability. Mental health issues can cause significant distress and impair an individual’s ability to perform daily tasks, leading to a decreased quality of life. This article will explore the definition of a mental health disability, the types of mental health issues that qualify as a disability, and the resources available to those who need to access disability benefits.
Mental health issues may be considered a disability under the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA). The ADA defines a disability as “a physical or mental impairment that substantially limits one or more major life activities of an individual.” Therefore, if a mental health issue significantly impacts a person’s life, it may be considered a disability.
Contents
- The Relationship Between Mental Health and Disability
- Top 6 Frequently Asked Questions
- What is a Mental Health Issue?
- What is a Disability?
- Are Mental Health Issues a Disability?
- What are Some Examples of Mental Health Issues That May be Considered Disabilities?
- Are There Laws that Protect People with Mental Health Issues?
- What Should I Do if I’m Experiencing Mental Health Issues?
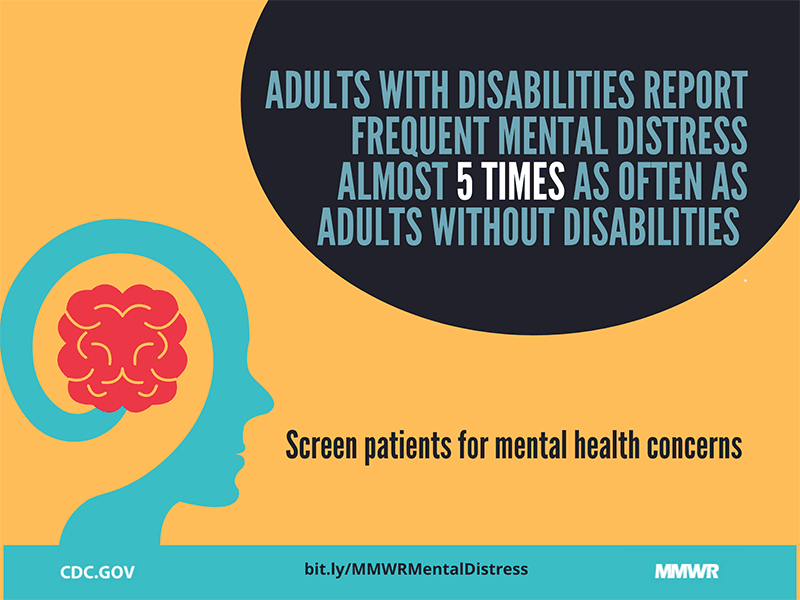
- Disabled people more likely to experience mental health issues | ABC News
- Is Diethylpropion A Stimulant?
- Is Alcohol A Inflammatory?
- Does Alcohol Make A Uti Worse?
The Relationship Between Mental Health and Disability
Mental health issues can be classified as disabilities under the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA). This means that people with mental health issues are afforded certain legal rights and protections, including protections against discrimination. Mental health conditions can range from being mild to severe, and can include conditions such as depression, anxiety, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), bipolar disorder, and schizophrenia.
Under the ADA, mental health issues are considered disabilities when they substantially limit one or more major life activities, such as learning, interacting with others, and caring for oneself. This means that people with mental health conditions may be eligible for reasonable accommodations in the workplace, such as flexible scheduling, modified work duties, or access to mental health services.
Mental health issues can also be seen as disabilities in other contexts, such as education. Students with mental health issues may be eligible for accommodations under Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act, which provides protections for students with disabilities. Examples of accommodations can include extended time on tests, access to note-takers, or modified grading standards.
Discrimination Against People with Mental Health Issues
Unfortunately, people with mental health issues are often discriminated against in the workplace and in other contexts. The ADA prohibits employers from discriminating against people with disabilities, including mental health issues. It is illegal for employers to ask questions about mental health status during a job interview, to refuse to hire someone because of a mental health condition, or to terminate someone because of a mental health condition.
Similarly, the ADA prohibits educational institutions from discriminating against students with mental health conditions. This includes denying them access to services, programs, or activities that are offered to other students, or treating them differently because of their mental health condition.
Protections for People with Mental Health Issues
In order to protect the rights of people with mental health issues, there are a number of laws in place. The ADA and Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act are both designed to protect people with disabilities, including those with mental health issues. Additionally, the Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA) provides job-protected leave for employees who need time off to attend to their mental health needs.
The Mental Health Parity and Addiction Equity Act (MHPAEA) is another law that protects people with mental health issues. This law prohibits health insurance plans from imposing different coverage limits or higher cost-sharing requirements for mental health services than for other medical services. It also requires that health plans cover mental health services at the same level as other medical services.
Conclusion
Mental health issues can be classified as disabilities under the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA). This means that people with mental health issues are afforded certain legal rights and protections, including protections against discrimination. Laws such as the ADA, Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act, the Family and Medical Leave Act (FMLA), and the Mental Health Parity and Addiction Equity Act (MHPAEA) are in place in order to protect the rights of people with mental health issues.
Top 6 Frequently Asked Questions
What is a Mental Health Issue?
A mental health issue is a health condition that involves changes in a person’s thinking, emotions, or behavior that can cause distress and problems functioning in social, work, or family activities. Mental health issues can range from mild to severe, and some of the most common mental health issues are depression, anxiety, bipolar disorder, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and schizophrenia.
What is a Disability?
A disability is a physical or mental impairment that significantly limits a person’s ability to perform major life activities such as hearing, seeing, speaking, walking, learning, and working. Disabilities can be visible, such as a physical disability, or invisible, such as mental health issues.
Are Mental Health Issues a Disability?
Yes, mental health issues can be considered a disability. According to the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA), mental health issues are considered a disability if they substantially limit a person’s ability to perform major life activities. This includes conditions like depression, anxiety, PTSD, bipolar disorder, and schizophrenia.
What are Some Examples of Mental Health Issues That May be Considered Disabilities?
Examples of mental health issues that may be considered disabilities can include depression, anxiety, bipolar disorder, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and schizophrenia. Other mental health issues such as obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), phobias, addictions, eating disorders, and personality disorders may also be considered disabilities, depending on their severity and how they limit a person’s ability to perform major life activities.
Are There Laws that Protect People with Mental Health Issues?
Yes, there are laws that protect people with mental health issues. The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) is a civil rights law that prohibits discrimination against people with disabilities in employment, public accommodations, transportation, and other areas. The ADA also protects people with mental health issues from discrimination in the workplace.
What Should I Do if I’m Experiencing Mental Health Issues?
If you are experiencing mental health issues, it’s important to seek help. Speak with a trusted friend or family member, contact a therapist, or reach out to an organization that specializes in mental health. The National Alliance on Mental Illness (NAMI) is a great resource for finding local mental health services and support. Additionally, it’s important to remember that you are not alone and there is help available.
Disabled people more likely to experience mental health issues | ABC News
In conclusion, mental health issues can be considered a disability. While each individual’s experience is unique and there is no one-size-fits-all definition, it is clear that mental health issues can have a significant impact on an individual’s health, wellbeing and quality of life. People with mental health issues should be treated with the same respect and understanding as people with any other kind of disability, and should be provided with the necessary care and resources to ensure their safety and wellbeing.
Francisco Church is a rehabilitation specialist and the chief editor of Recovery Ranger. He creates this site to offer guidance and support to individuals seeking to overcome addiction and achieve lasting sobriety. With extensive experience in the field of addiction treatment, Francisco is dedicated to helping individuals access the resources they need for successful recovery.
- Latest Posts by Francisco Church
-
Is Diethylpropion A Stimulant?
- -
Is Alcohol A Inflammatory?
- -
Does Alcohol Make A Uti Worse?
- All Posts