Francisco Church is a rehabilitation specialist and the chief editor of Recovery Ranger. He creates this site to offer guidance and support to individuals seeking...Read more
Alcohol is a substance that has been around for centuries, but what is the science behind why it can be so addictive? Recent studies have shown that alcohol is actually composed of numerous chemicals that cause a range of physical and psychological effects, and some of these components make it particularly addictive. This article will explore what is in alcohol that makes it so addictive and how to recognize and address an addiction to it.
Alcohol is addictive due to its effects on the brain and body. It causes changes in the brain that make people crave alcohol and increases the risk of developing an addiction. Alcohol also has an effect on the body, causing physical and psychological dependence. This makes it difficult for people to stop drinking once they start.
Alcohol affects the way the brain works by altering the activity of neurotransmitters, the chemicals that carry messages between brain cells. It increases the levels of the neurotransmitter dopamine, which is linked to the reward system in the brain and makes people feel good. It also increases the production of endorphins, which are linked to pleasure.
Alcohol also affects the body by causing physical dependence. This is when the body becomes used to alcohol and needs it to function normally. People who are dependent on alcohol can experience withdrawal symptoms when they stop drinking, such as anxiety, tremors, and sweating.
These changes in the brain and body can lead to alcohol addiction, which is a chronic and relapsing condition. It can be treated with therapy, medications, and support groups.
Contents
- What Makes Alcohol Addictive?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- What are the components of alcohol that make it addictive?
- How does ethanol affect the brain?
- What are congeners and how do they affect addiction?
- What role do sugars play in alcohol addiction?
- Are there long-term effects of alcohol addiction?
- What treatments are available for alcohol addiction?
- Are You Addicted to Alcohol?
- Is Diethylpropion A Stimulant?
- Is Alcohol A Inflammatory?
- Does Alcohol Make A Uti Worse?
What Makes Alcohol Addictive?
Alcohol is a psychoactive substance that can be highly addictive. It has been linked to a variety of health and social problems, including an increased risk of certain types of cancer and other diseases. While alcohol can be consumed in moderation, drinking too much can cause physical and psychological dependence. So, what is it about alcohol that makes it so addictive?
Alcohol is a depressant that affects the central nervous system. It can produce a pleasurable feeling of relaxation or euphoria. This can be very appealing to those looking to reduce stress or escape from reality. Additionally, alcohol’s intoxicating effects can make it easier to socialize. This can be an attractive factor for those who are socially anxious or lack self-confidence.
The brain is also affected by alcohol. It can increase the release of dopamine, which is a neurotransmitter associated with pleasure. This can lead to the development of a positive reinforcement cycle where the user begins to crave alcohol more and more to achieve the same level of pleasure.
Alcohol Tolerance
Alcohol tolerance is another factor that can contribute to alcohol addiction. As a person drinks more and more, their body will become accustomed to the effects of alcohol. This means that they will need to consume more alcohol to achieve the same level of intoxication. This can lead to an increased risk of alcohol poisoning, as well as an increased risk of developing an alcohol addiction.
Alcohol can also be physically addictive. Long-term alcohol consumption can cause changes in the brain that make it difficult to stop drinking. This can lead to the development of physical withdrawal symptoms when alcohol consumption is stopped. These symptoms can range from mild to severe, and can include headaches, nausea, tremors, and anxiety.
Alcohol Abuse
Alcohol abuse is a major risk factor for developing an alcohol addiction. People who abuse alcohol are more likely to develop a tolerance to the substance, as well as physical and psychological dependence. This can lead to increased alcohol consumption and an increased risk of health complications.
People can also become psychologically dependent on alcohol. This can be seen when people rely on alcohol to cope with stress, anxiety, or depression. This can be a dangerous situation, as people may feel that they need alcohol to cope with their emotions. This can lead to increased alcohol consumption and an increased risk of developing an alcohol addiction.
Social Factors
Social factors can also play a role in alcohol addiction. People may feel pressure from their peers to drink, or may feel that drinking is an acceptable way to fit in. Additionally, people may use alcohol as a way to cope with social anxiety or other social issues.
Cultural and environmental factors can also contribute to alcohol addiction. In some cultures, alcohol consumption is seen as a normal or even necessary part of life. Additionally, people who are exposed to alcohol at a young age are more likely to develop an alcohol addiction later in life.
Genetics
Genetics can also be a factor in alcohol addiction. Studies have shown that people with a family history of alcohol addiction are more likely to develop an alcohol addiction themselves. Additionally, people with certain genetic variations may be more likely to develop an alcohol addiction due to an increased sensitivity to the substance.
Treatment
Treatment for alcohol addiction can involve a combination of medication, therapy, and support groups. Medications such as naltrexone and acamprosate can help reduce cravings and make it easier to abstain from alcohol. Therapy can help the individual identify underlying issues that may be contributing to their drinking, as well as work on developing healthier coping skills. Support groups can provide individuals with a safe and supportive environment to discuss their experiences and receive support from others who are also in recovery.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the components of alcohol that make it addictive?
Alcohol is made up several components, most notably ethanol. Ethanol is a central nervous system depressant, and it is the component that is largely responsible for the intoxication, or drunkenness, that is associated with alcohol consumption. Other components of alcohol, such as congeners, can contribute to the flavor and aroma of alcoholic drinks, and may also play a role in the addiction potential of alcohol. Additionally, alcohol also contains sugars, which can contribute to cravings and the addictive nature of alcohol.
How does ethanol affect the brain?
Ethanol affects the brain by binding to neurotransmitter systems, including those that are responsible for pleasure, reward and motivation. When a person consumes alcohol, it causes the release of the neurotransmitter dopamine, resulting in the pleasurable sensations associated with drinking. Over time, this can result in changes to the brain associated with addiction, such as an increased tolerance to the effects of alcohol and withdrawal symptoms when not drinking.
What are congeners and how do they affect addiction?
Congeners are compounds found in alcohol that contribute to the flavor and aroma of alcoholic drinks, but they can also contribute to the addictive nature of alcohol. Congeners are more prevalent in darker colored drinks, such as whiskey, brandy, and red wine, and they can increase the intoxicating effects of alcohol. Studies have also suggested that congeners may increase the risk of developing an alcohol use disorder, as well as the severity of withdrawal symptoms.
What role do sugars play in alcohol addiction?
Sugars play an important role in alcohol addiction, as they can contribute to cravings and addiction potential. Studies have shown that alcohol consumption leads to increased levels of dopamine and other neurotransmitters, which can lead to cravings for more alcohol. Additionally, alcohol contains sugars, which can further increase cravings and the risk of addiction.
Are there long-term effects of alcohol addiction?
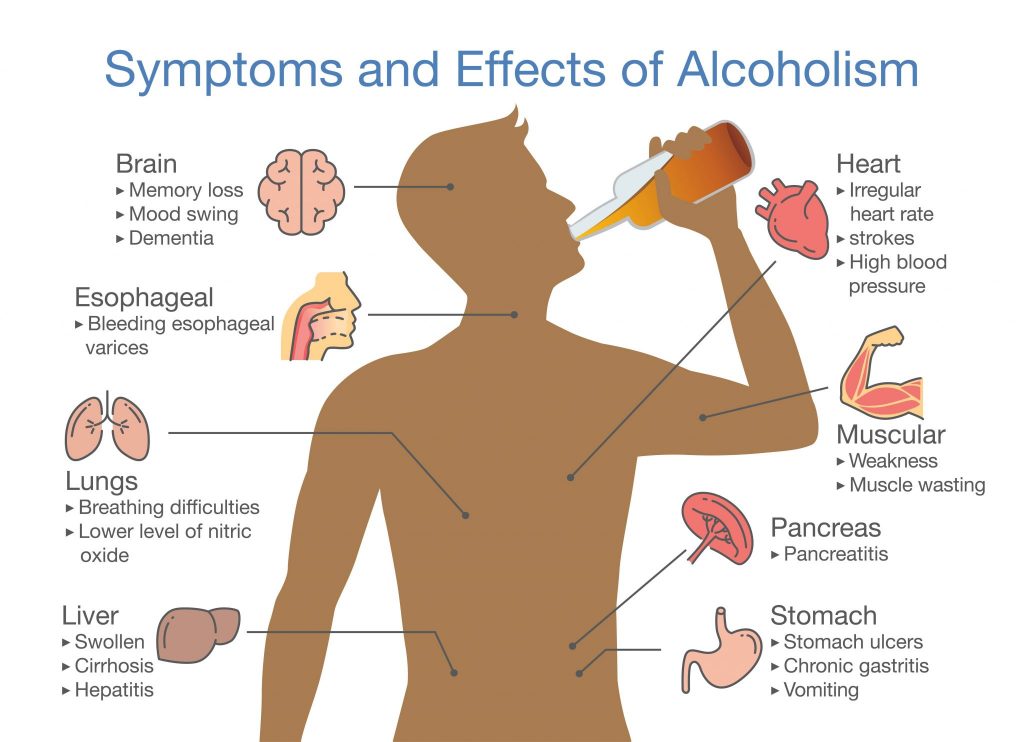
Yes, there are a variety of long-term effects associated with alcohol addiction. Long-term alcohol use can lead to a variety of health problems, including liver damage, cardiovascular disease, and an increased risk of certain types of cancer. Additionally, long-term alcohol use can lead to changes in the brain associated with addiction, such as an increased tolerance to the effects of alcohol and withdrawal symptoms when not drinking.
What treatments are available for alcohol addiction?
There are a variety of treatments available for alcohol addiction, depending on the individual and the severity of their addiction. Some of the most common treatments include psychotherapy, medication, and support groups. In some cases, a combination of treatments may be recommended. Additionally, lifestyle changes, such as avoiding triggers, limiting alcohol consumption, and engaging in healthy activities, can also help to reduce the risk of relapse.
Are You Addicted to Alcohol?
Overall, alcohol is a powerful substance that can have both positive and negative effects on individuals. It can lead to addiction and other health issues if not managed properly. While the exact answer to what makes alcohol addictive is still unknown, we do know that it is a complex mixture of physical, psychological and environmental factors. With appropriate measures, it is possible to manage alcohol use and lead a healthier lifestyle.
Francisco Church is a rehabilitation specialist and the chief editor of Recovery Ranger. He creates this site to offer guidance and support to individuals seeking to overcome addiction and achieve lasting sobriety. With extensive experience in the field of addiction treatment, Francisco is dedicated to helping individuals access the resources they need for successful recovery.
- Latest Posts by Francisco Church
-
Is Diethylpropion A Stimulant?
- -
Is Alcohol A Inflammatory?
- -
Does Alcohol Make A Uti Worse?
- All Posts