Francisco Church is a rehabilitation specialist and the chief editor of Recovery Ranger. He creates this site to offer guidance and support to individuals seeking...Read more
Benzodiazepines are a class of medications that have been used to treat anxiety, insomnia, and various other conditions for decades. But what exactly do these drugs do in the brain to produce these effects? In this article, we will explore how benzodiazepines work in the brain and why they are so effective in treating a variety of conditions.
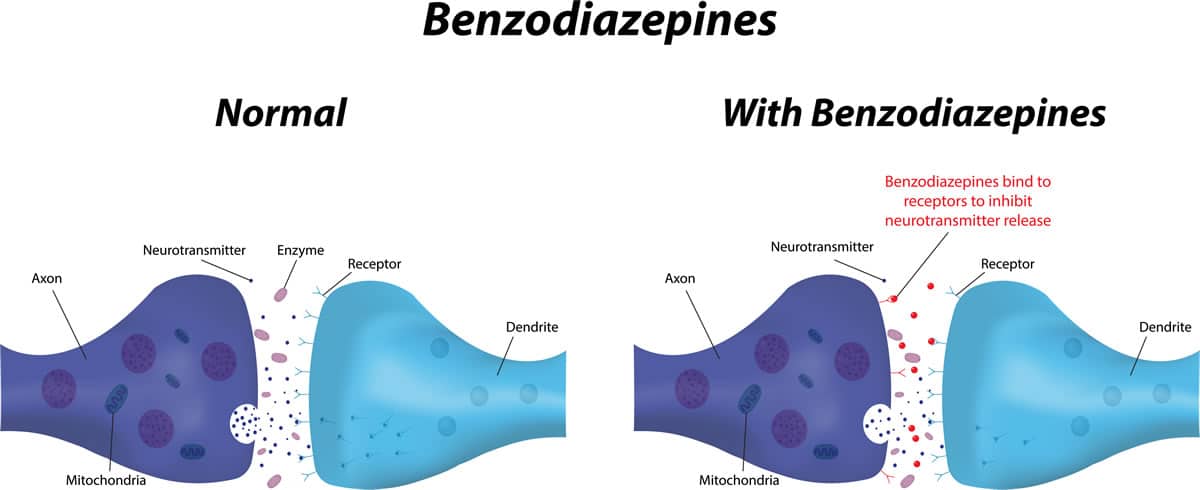
Benzodiazepines work by increasing the activity of the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in the brain. GABA is a chemical messenger that helps reduce the activity of nerve cells in the brain, leading to a feeling of relaxation and decreased anxiety. Benzodiazepines attach to specific receptors in the brain, which then increase the effect of GABA, leading to a calming effect.
Contents
- What Are Benzodiazepines?
- Treatment for Benzodiazepine Abuse and Addiction
- Top 6 Frequently Asked Questions
- What are Benzodiazepines?
- How do Benzodiazepines Work in the Brain?
- What are the Side Effects of Benzodiazepines?
- What are the Benefits of Taking Benzodiazepines?
- Are There Alternatives to Taking Benzodiazepines?
- Are Benzodiazepines Safe?
- 2-Minute Neuroscience: Benzodiazepines
- Is Diethylpropion A Stimulant?
- Is Alcohol A Inflammatory?
- Does Alcohol Make A Uti Worse?
What Are Benzodiazepines?
Benzodiazepines are a class of drugs that are commonly prescribed to treat a variety of medical conditions, including anxiety, insomnia, seizures, and muscle spasms. They are one of the most commonly prescribed medications in the United States. Benzodiazepines work by enhancing the effects of the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in the brain. GABA is a chemical messenger that helps regulate mood and anxiety. By increasing the activity of GABA, benzodiazepines produce a calming effect.
Benzodiazepines are generally considered safe and effective when taken as prescribed. However, they can be habit-forming and have the potential for abuse and addiction. Long-term use of benzodiazepines can also lead to tolerance, meaning that higher doses are needed to achieve the same effect.
How Benzodiazepines Work in the Brain
Benzodiazepines work by binding to GABA receptors in the brain, increasing the activity of GABA and producing a calming effect. GABA is an inhibitory neurotransmitter, which means it reduces the activity of neurons in the brain. By increasing the activity of GABA, benzodiazepines can reduce the excitability of neurons and decrease the symptoms of anxiety, insomnia, and seizures.
Benzodiazepines also affect the part of the brain known as the limbic system, which plays a role in emotion and motivation. By affecting this area of the brain, benzodiazepines can reduce anxiety and improve mood.
Side Effects of Benzodiazepines
Although benzodiazepines are generally safe and effective when taken as prescribed, they can cause a variety of side effects. Common side effects of benzodiazepines include drowsiness, dizziness, confusion, and blurred vision. They can also cause muscle weakness, dry mouth, and impaired coordination.
Long-term use of benzodiazepines can lead to tolerance, meaning that higher doses are needed to achieve the same effect. As a result, people who take benzodiazepines for an extended period of time may be at risk of developing physical dependence on the drug.
Risks of Misuse and Abuse
Benzodiazepines are generally safe and effective when taken as prescribed, but they can be habit-forming and have the potential for abuse and addiction. Misuse and abuse of benzodiazepines can lead to serious side effects, including respiratory depression, coma, and even death.
Mixing benzodiazepines with alcohol or other drugs can be especially dangerous and can increase the risk of overdose. People who misuse or abuse benzodiazepines may also be at risk of developing a psychological dependence on the drug.
Treatment for Benzodiazepine Abuse and Addiction
If you or someone you know is abusing or addicted to benzodiazepines, it is important to seek professional help. Treatment for benzodiazepine abuse and addiction typically begins with a medically supervised detox, which can help reduce the symptoms of withdrawal.
After detox, the next step is typically an inpatient or outpatient treatment program. Treatment programs typically involve counseling, therapy, and other supportive services. These services can help individuals develop healthier coping strategies and learn how to manage their symptoms without the use of drugs.
Medication-Assisted Treatment
Medication-assisted treatment is another option for treating benzodiazepine abuse and addiction. This type of treatment typically involves the use of medications, such as naltrexone or buprenorphine, to reduce cravings and help individuals stay in recovery.
Self-Help Groups
Self-help groups, such as 12-step programs, can also be a helpful resource for individuals who are struggling with benzodiazepine abuse and addiction. These groups provide a supportive environment where individuals can share their experiences and learn from others who are in recovery.
Top 6 Frequently Asked Questions
What are Benzodiazepines?
Benzodiazepines are a class of drugs that are commonly prescribed to treat a variety of conditions, including anxiety, insomnia, and seizures. These drugs act on the central nervous system, producing calming effects and reducing symptoms of these conditions. Benzodiazepines work by binding to receptors in the brain, known as GABA receptors, and increasing the activity of the inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA, which reduces fear and anxiety.
How do Benzodiazepines Work in the Brain?
Benzodiazepines work in the brain by binding to GABA receptors, which are found in the brain’s hippocampus and amygdala. This binding causes an increase in the activity of the inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA. This increased activity has a calming effect on the body, reducing symptoms of anxiety and other conditions.
What are the Side Effects of Benzodiazepines?
The most common side effects of benzodiazepines include drowsiness, dizziness, confusion, impaired coordination, impaired judgment, and impaired memory. Long-term use of benzodiazepines can also result in physical dependence and tolerance, which can lead to withdrawal symptoms when the drug is stopped.
What are the Benefits of Taking Benzodiazepines?
The primary benefit of taking benzodiazepines is that they can help to reduce symptoms of anxiety and other conditions. They can also be used to help treat insomnia and seizures. Benzodiazepines can be a useful tool for helping to manage these conditions in the short-term.
Are There Alternatives to Taking Benzodiazepines?
Yes, there are alternatives to taking benzodiazepines. Some of these alternatives include psychotherapy, relaxation techniques, and lifestyle changes. Additionally, some medications, such as SSRIs (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors), can also be used to treat anxiety and other conditions.
Are Benzodiazepines Safe?
Benzodiazepines can be safe when taken as prescribed, but they can be dangerous when taken in large amounts or combined with other drugs or alcohol. They can also be habit-forming, so it is important to take them only as prescribed and not to take more than the recommended dose. It is also important to talk to your doctor about the risks and benefits of taking benzodiazepines before beginning treatment.
2-Minute Neuroscience: Benzodiazepines
In conclusion, benzodiazepines are a powerful class of medications that affect brain chemistry in a variety of ways. They work by increasing GABA activity, which helps to reduce anxiety, improve sleep, and reduce muscle tension. They also affect other brain chemicals, such as serotonin and dopamine, which can lead to a range of other effects. While benzodiazepines are effective for treating a variety of conditions, they should be used with caution, as they can lead to dependence and withdrawal symptoms. When used responsibly, however, they can provide an effective and safe way to manage anxiety and other mental health issues.
Francisco Church is a rehabilitation specialist and the chief editor of Recovery Ranger. He creates this site to offer guidance and support to individuals seeking to overcome addiction and achieve lasting sobriety. With extensive experience in the field of addiction treatment, Francisco is dedicated to helping individuals access the resources they need for successful recovery.
- Latest Posts by Francisco Church
-
Is Diethylpropion A Stimulant?
- -
Is Alcohol A Inflammatory?
- -
Does Alcohol Make A Uti Worse?
- All Posts